第六节: Dubbo服务引入源码解析
过程
当Spring启动过程中,会去给@Reference注解标注了的属性去进行赋值,赋值的对象为ReferenceBean中get()方法所返回的对象,这个对象是一个代理对象。
对于ReferenceBean,它表示应用想要引入的服务的信息,在执行get()时会做如下几步:
-
调用checkAndUpdateSubConfigs(),检查和更新参数,和服务提供者类似,把ReferenceBean里的属性的值更新为优先级最高的参数值
-
调用init()去生成代理对象ref,get()方法会返回这个ref
-
在生成代理对象ref之前,先把消费者所引入服务设置的参数添加到一个map中,等会根据这个map中的参数去从注册中心查找服务
-
把消费者配置的所有注册中心获取出来
- 如果只有一个注册中心,那么直接调用Protocol的refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));得到一个Invoker对象
- 如果有多个注册中心,则遍历每个注册中心,分别调用Protocol的refer(interfaceClass, url);得到一个Invoker对象添加到invokers中,然后把invokers调用CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));封装所有invokers得到一个invoker,
-
把最终得到的invoker对象调用PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);得到一个代理对象,并返回,这个代理对象就是ref
-
总结:上文的Invoker对象,表示服务执行者,从注册中心refer下来的是一个服务执行者,合并invokers后得到的invoker也是一个服务执行者(抽象范围更大了)
接下来,来看Protorol.refer(interfaceClass, url)方法是怎么生成一个Invoker的
-
首先interfaceClass表示要引入的服务接口,url是注册中心的url(registry://),该url中有一个refer参数,参数值为当前所要引入服务的参数
-
调用doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url)
-
在doRefer方法中会生成一个RegistryDirectory
-
然后获取新版本中的路由器链,并添加到RegistryDirectory中去
-
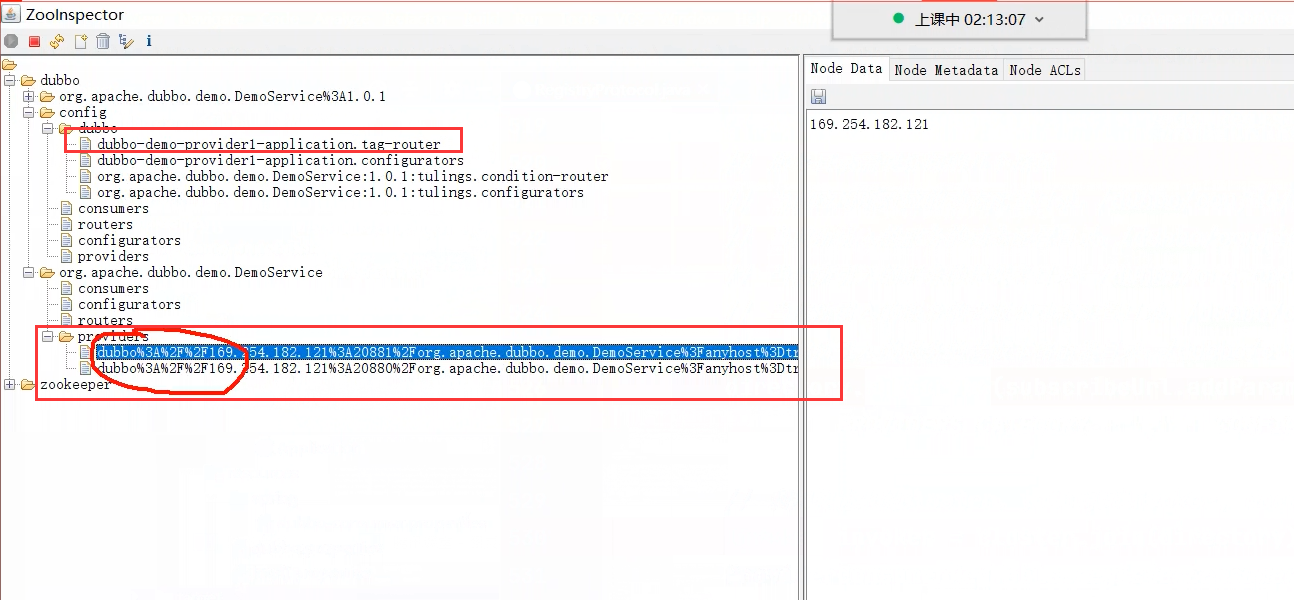
RegistryDirectory监听几个目录(注意,完成监听器的订阅绑定后,会自动触发一次去获取这些目录上的当前数据)
- 当前所引入的服务的动态配置目录:/dubbo/config/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService:1.1.1:g1.configurators
- 当前所引入的服务的提供者目录:/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/providers
- 当前所引入的服务的老版本动态配置目录:/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators
- 当前所引入的服务的老版本路由器目录:/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/routers
-
调用cluster.join(directory)得到一个invoker
-
返回invoker(如果消费者引入了多个group中的服务,那么这里返回的是new MergeableClusterInvoker
(directory);,否则返回的是new FailoverClusterInvoker (directory);) -
但是,上面返回的两个Invoker都会被MockClusterInvoker包装,所以最终返回的是MockClusterInvoker。
Dubbo官方给的Demo
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*/
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("demoServiceComponent")
public class DemoServiceComponent implements DemoService {
@Reference(version = "1.0.1", group = "youthlql", mock = "fail: return 123")
private DemoService demoService;
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return demoService.sayHello(name); // Invoker
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*/
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp.DemoServiceComponent;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.service.EchoService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Application {
/**
* In order to make sure multicast registry works, need to specify '-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true' before
* launch the application
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConsumerConfiguration.class);
context.start();
DemoService service = context.getBean("demoServiceComponent", DemoServiceComponent.class);
System.out.println("开始调用");
String hello = service.sayHello("world");
System.out.println("result :" + hello);
System.in.read();
}
@Configuration
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp")
@PropertySource("classpath:/spring/dubbo-consumer.properties")
@ComponentScan(value = {"org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer.comp"})
static class ConsumerConfiguration {
@Bean
public ConsumerConfig consumerConfig() {
return new ConsumerConfig();
}
}
}
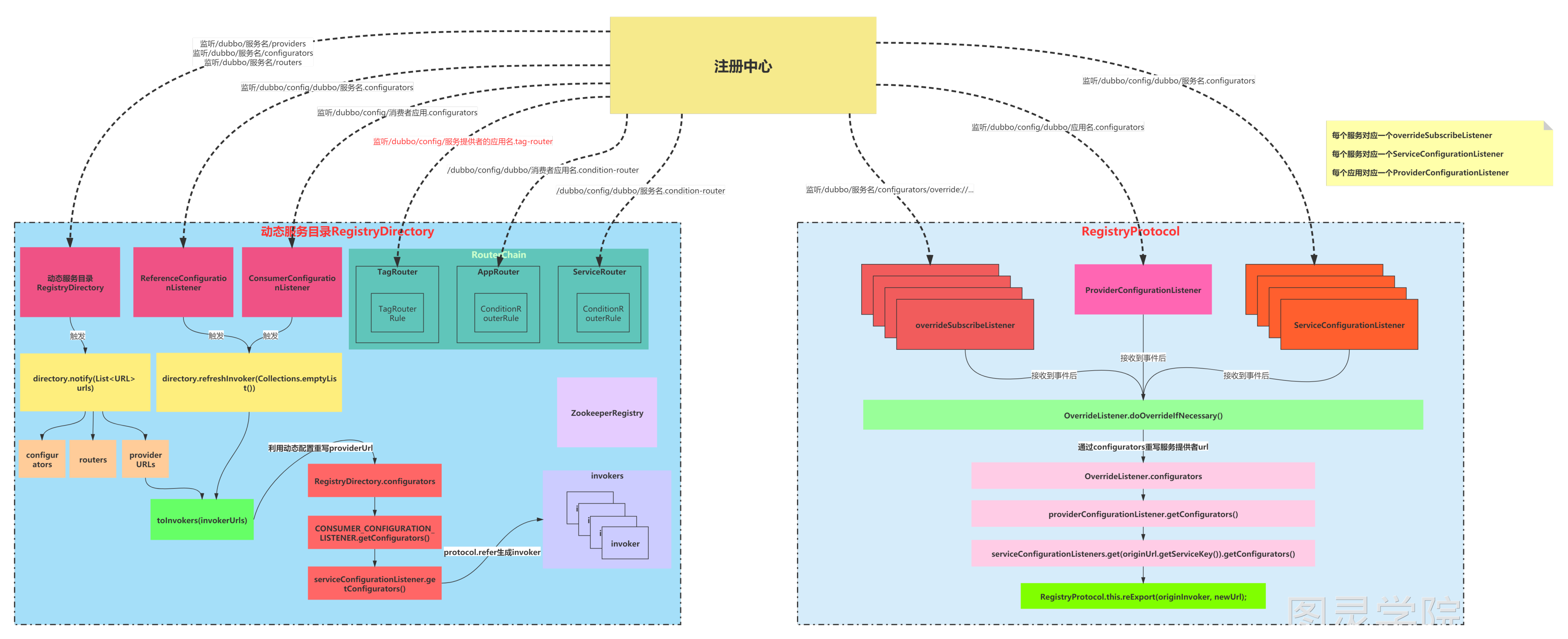
服务引入过程概述
什么是服务引入
- 首先服务引入的意思:在Spring启动的时候去扫描那个@Reference注解标注的Bean,把它注入到容器中,并且去构建一下服务真正调用时候的一些必要东西,比如调用哪个IP哪个端口的哪个服务实例,这样的东西叫做服务目录。
- 注意服务目录是需要提前构建到本地,不能等你调用的时候再去注册中心获取,这样会很慢。从这个角度来说,服务目录相当于把注册中心上关于服务提供者的信息提前缓存到本地,只不过做了一些转化。
- 总的来说,服务引入的目的就是构建服务目录
- 每一个服务提供者的接口都有一个服务目录,比如我们用@Reference标记了DemoService和MyService两个服务提供者,那么这两个服务提供者都有自己的服务目录
消费端每个服务对应一个服务目录RegistryDirectory。
一个服务目录中包含了:
- serviceType:表示服务接口
- serviceKey:表示引入的服务key,serviceclass+version+group
- queryMap:表示引入的服务的参数配置
- configurators:动态配置
- routerChain:路由链
- invokers:表示服务目录当前缓存的服务提供者Invoker
- ConsumerConfigurationListener:监听本应用的动态配置
- ReferenceConfigurationListener:监听所引入的服务的动态配置
大致的步骤
- 解析@Reference注解上的一些配置,生成URL
- 监听注册中心并拉取注册中心上相关的配置。
- 服务启动时的-D参数,并且从注册中心上拉取web端的动态配置。这些参数配置根据优先级顺序覆盖掉注册中心上服务提供者的配置。优先级的话前面也讲过web端的动态配置 > -D参数 > @Reference注解 > @Services生成的提供者URL。
- 注册中心上也包括了路由链的配置
- 监听。首先服务目录就是把注册中心上的信息缓存到了本地,所以如果注册中心上信息变了,本地的服务目录也要随之更新,也就是需要监听。
- 把上面几步整合的URL转成
List<DubboInvoker>。List<DubboInvoker>才是真正要用的
监听
在服务消费端有几个监听器:
-
ConsumerConfigurationListener:监听本应用的动态配置,当应用的动态配置发生了修改后,会调用RegistryDirectory的refreshInvoker()方法,对应的路径为:"/dubbo/config/dubbo/dubbo-demo-consumer-application.configurators"
-
ReferenceConfigurationListener:监听所引入的服务的动态配置,当服务的动态配置发生了修改后,会调用RegistryDirectory的refreshInvoker()方法,对应的路径为:"/dubbo/config/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService:1.1.1:g1.configurators"
-
RegistryDirectory:RegistryDirectory本身也是一个监听器,它会监听所引入的服务提供者、服务动态配置(老版本)、服务路由,路径分别为:
- "/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/providers"
- "/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators"
- "/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/routers"
-
路由器Router:每个Router自己本身也是一个监听器,负责监听对应的路径
- AppRouter:应用路由,监听的路径为**"/dubbo/config/dubbo/dubbo-demo-consumer-application.condition-router"**
- ServiceRouter: 服务路由,监听的路径为**"/dubbo/config/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService:1.1.1:g1.condition-router"**
- TagRouter: 标签路由,标签路由和应用路由、服务路由有所区别,应用路由和服务路由都是在消费者启动,在构造路由链时会进行监听器的绑定,但是标签路由不是消费者启动的时候绑定监听器的,是在引入服务时,获取到服务的提供者URL之后,才会去监听.tag-router节点中的内容,监听的路径为**"/dubbo/config/dubbo/dubbo-demo-provider-application.tag-router"**
-
当ConsumerConfigurationListener接收到了消费者应用的动态配置数据变化后,会调用当前消费者应用中的所有RegistryDirectory的refreshInvoker()方法,表示刷新消费者应用中引入的每个服务对应的Invoker
-
当ReferenceConfigurationListener接收到了某个服务的动态配置数据变化后,会调用该服务对应的RegistryDirectory的refreshInvoker()方法,表示刷新该服务对应的Invoker
-
当AppRouter和ServiceRouter接收到条件路由的数据变化后,就会更新Router内部的routerRule和conditionRouters属性。这两个属性在服务调用过程中会用到。
-
当TagRouter接收到标签路由的数据变化后,就会更新TagRouter内部的tagRouterRule的属性,这个属性在服务调用过程中会用到。
-
当RegistryDirectory接收到"/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators"节点数据变化后,会生成configurators
-
当RegistryDirectory接收到"/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/routers“节点数据变化后,会生成Router并添加到routerChain中
-
当RegistryDirectory接收到”/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/providers“节点数据变化后,会调用refreshOverrideAndInvoker()方法。这个方法就是用来针对每个服务提供者来生成Invoker的。
- refreshOverrideAndInvoker方法中首先调用overrideDirectoryUrl()方法利用Configurators重写目录地址,目录地址是这样的:
zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=dubbo-demo-consumer-application&dubbo=2.0.2&group=g1&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&lazy=false&methods=sayHello&pid=49964®ister.ip=192.168.40.17&release=2.7.0&revision=1.1.1&side=consumer&sticky=false×tamp=1591339005022&version=1.1.1,在注册中心URL基础上把当前引入服务的参数作为URL的Parameters,所以这个地址既包括了注册中心的信息,也包括了当前引入服务的信息 - 利用老版本configurators,Consumer应用的configurators,引入的服务的configurators去重写目录地址。
- 重写往目录地址后,调用refreshInvoker(urls)方法去刷新Invoker
- 在refreshInvoker(urls)方法中会把从注册中心获取到的providers节点下的服务URL,调用toInvokers(invokerUrls)方法得到Invoker
- 先按Protocol进行过滤,并且调用DubboProtocol.refer方法得到Invoker
- 将得到的invokers设置到RouterChain上,并且调用RouterChain上所有的routers的notify(invokers)方法,实际上这里只有TagRouter的notify方法有用
- 再把属于同一个group中的invoker合并起来
- 这样Invoker就生成好了
- refreshOverrideAndInvoker方法中首先调用overrideDirectoryUrl()方法利用Configurators重写目录地址,目录地址是这样的:
源码分析-解析@Reference注解上的配置
ReferenceBean
/**
* 1.这里是入口方法,Spring容器在启动时就会先生成ReferenceBean对象,接着会调用{@link ReferenceConfig#get()}
* 2.意思就是当你标注了注解@Reference,Spring启动扫描bean的时候会调用此类重写的
* {@link ReferenceBean#afterPropertiesSet()},最终会调到get()返回一个代理对象给那个bean
* 3.也就是说在调用此方法之前,ReferenceBean对象就已经生成了,里面的属性值也都有了。
*/
@Override
public Object getObject() {
// 这里调用ReferenceConfig#get()
return get();
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//前面代码太长了,省略...
if (shouldInit()) {
getObject();
}
ReferenceConfig
public synchronized T get() {
checkAndUpdateSubConfigs();
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The invoker of ReferenceConfig(" + url + ") has already destroyed!");
}
/**
* 前面讲过{@link ReferenceConfig#ref}属性就是代理对象
*/
if (ref == null) {
// 入口,这里就是核心了
init();
}
return ref; // 返回的是Invoke代理
}
private void init() {
if (initialized) {
return;
}
//代码太长省略了,主要就是跟服务导出一样,准备参数。比如@Reference注解里的属性还有properties的配置参数等
// 关键
ref = createProxy(map);
String serviceKey = URL.buildKey(interfaceName, group, version);
ApplicationModel.initConsumerModel(serviceKey, buildConsumerModel(serviceKey, attributes));
initialized = true;
}
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// injvm://
URL url = new URL(LOCAL_PROTOCOL, LOCALHOST_VALUE, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
// 为什么会有urls,因为可以在@Reference的url属性中配置多个url,可以是点对点的服务地址,也可以是注册中心的地址
urls.clear(); // reference retry init will add url to urls, lead to OOM
// @Reference中指定了url属性,
// @Reference上标注的属性是在Spring启动时就扫描进了相应的属性里,所以这里如果配置了就会有
// 前面讲过扫描到这些东西赋值给对应的属性
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address.
String[] us = SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url); // 用;号切分
if (us != null && us.length > 0) {
for (String u : us) {
URL url = URL.valueOf(u);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(url.getPath())) {
url = url.setPath(interfaceName);
}
// 如果是注册中心地址,则在url中添加一个refer参数
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
// map表示消费者端配置的参数
urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
} else {
// 如果是服务地址
// 有可能url中配置了参数,map中表示的服务消费者消费服务时的参数,所以需要合并
urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map));
}
}
}
} else { // assemble URL from register center's configuration
// @Reference中的protocol属性表示使用哪个协议调用服务,如果不是本地调用协议injvm://,则把注册中心地址找出来
// 对于injvm://协议已经在之前的逻辑中就已经生成invoke了
// if protocols not injvm checkRegistry
if (!LOCAL_PROTOCOL.equalsIgnoreCase(getProtocol())) {
checkRegistry();
// 加载注册中心地址
List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(us)) {
for (URL u : us) {
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
map.put(MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
}
// 对于注册中心地址都添加REFER_KEY
urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
}
}
if (urls.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config.");
}
}
}
/**
* 1.如果URL是registry,表明这是注册中心相关的调用进来的,一般来说注册中心只有一个,
* 就会进入这个方法
* 2.下面还是会用到SPI机制,就是首先调用Protocol接口的两个wrapper包装。debug时候的顺序是
* ProtocolListenerWrapper -> ProtocolFilterWrapper
* 3.然后根据SPI机制,由于URL是Registry,就调用RegistryProtocol.refer()
*/
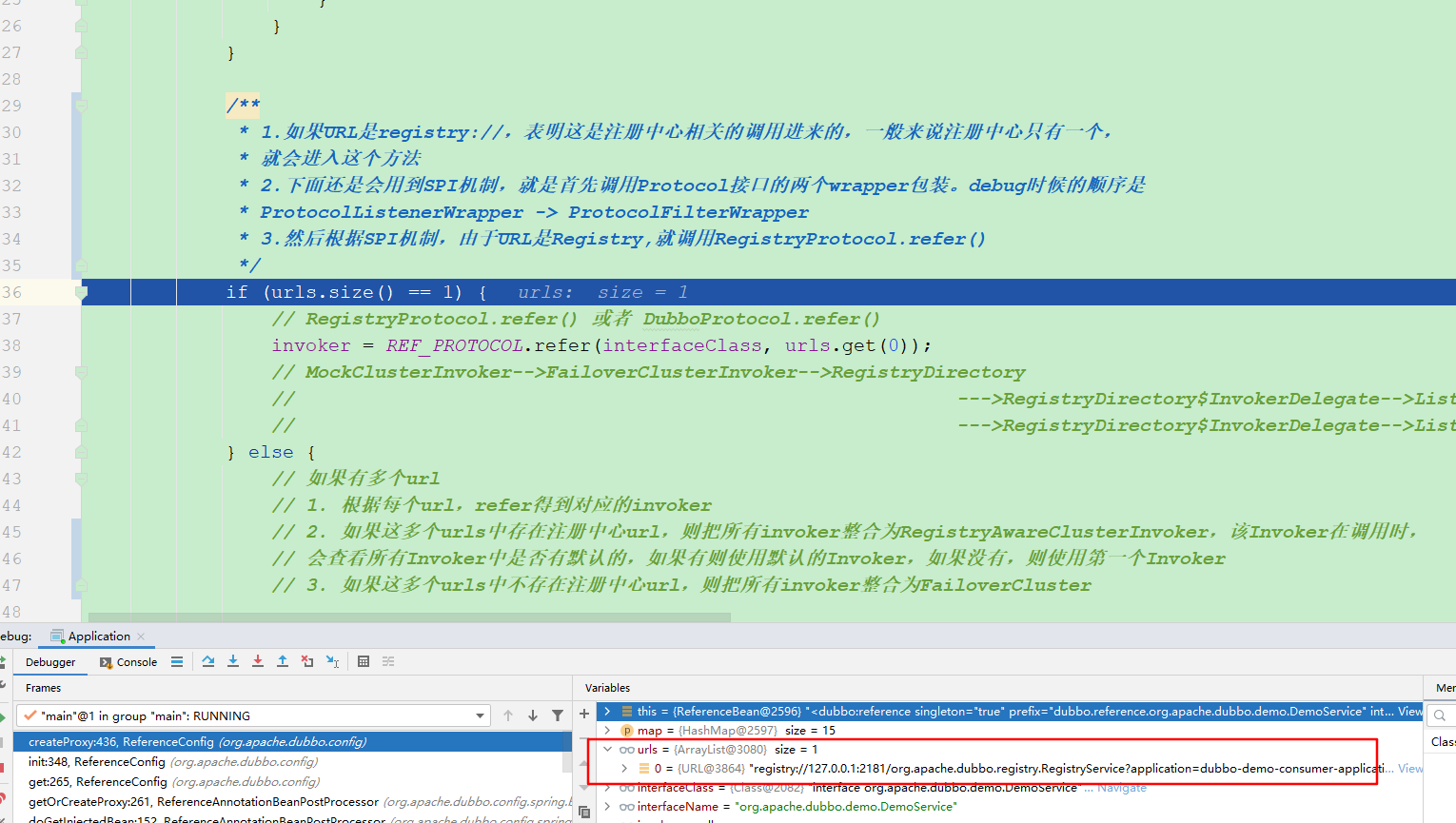
if (urls.size() == 1) {
// RegistryProtocol.refer() 或者 DubboProtocol.refer()
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
// MockClusterInvoker-->FailoverClusterInvoker-->RegistryDirectory
// --->RegistryDirectory$InvokerDelegate-->ListenerInvokerWrapper-->ProtocolFilterWrapper$CallbackRegistrationInvoker-->ConsumerContextFilter-->FutureFilter-->MonitorFilter-->AsyncToSyncInvoker-->DubboInvoker
// --->RegistryDirectory$InvokerDelegate-->ListenerInvokerWrapper-->ProtocolFilterWrapper$CallbackRegistrationInvoker-->ConsumerContextFilter-->FutureFilter-->MonitorFilter-->AsyncToSyncInvoker-->DubboInvoker
} else {
// 如果有多个url
// 1. 根据每个url,refer得到对应的invoker
// 2. 如果这多个urls中存在注册中心url,则把所有invoker整合为RegistryAwareClusterInvoker,该Invoker在调用时,
// 会查看所有Invoker中是否有默认的,如果有则使用默认的Invoker,如果没有,则使用第一个Invoker
// 3. 如果这多个urls中不存在注册中心url,则把所有invoker整合为FailoverCluster
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null; // 用来记录urls中最后一个注册中心url
for (URL url : urls) {
invokers.add(REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url));
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
// 如果存在注册中心地址
if (registryURL != null) { // registry url is available
// use RegistryAwareCluster only when register's CLUSTER is available
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(CLUSTER_KEY, RegistryAwareCluster.NAME);
// StaticDirectory表示静态服务目录,里面的invokers是不会变的, 生成一个RegistryAwareCluster
// The invoker wrap relation would be: RegistryAwareClusterInvoker(StaticDirectory) -> FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, will execute route) -> Invoker
/**
*
* {@link org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.wrapper.MockClusterWrapper#join(Directory)}
* {@link org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.wrapper.MockClusterInvoker}
* {@link RegistryAwareCluster}
* {@link org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.RegistryAwareClusterInvoker}
* 1.这里会先调用MockClusterWrapper#join生成一个MockClusterInvoker(为什么先调用wrapper前面讲过)
* 2.接着在MockClusterWrapper#join方法中会继续调用join方法,通过SPI机制,实际调用的是
* RegistryAwareCluster生成RegistryAwareClusterInvoker
*
*/
invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else { // not a registry url, must be direct invoke.
// 如果不存在注册中心地址, 生成一个FailoverClusterInvoker
invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
if (shouldCheck() && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to check the status of the service " + interfaceName + ". No provider available for the service " + (group == null ? "" : group + "/") + interfaceName + (version == null ? "" : ":" + version) + " from the url " + invoker.getUrl() + " to the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl());
}
/**
* @since 2.7.0
* ServiceData Store
*/
MetadataReportService metadataReportService = null;
if ((metadataReportService = getMetadataReportService()) != null) {
URL consumerURL = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, map.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, map.get(INTERFACE_KEY), map);
metadataReportService.publishConsumer(consumerURL);
}
// create service proxy
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
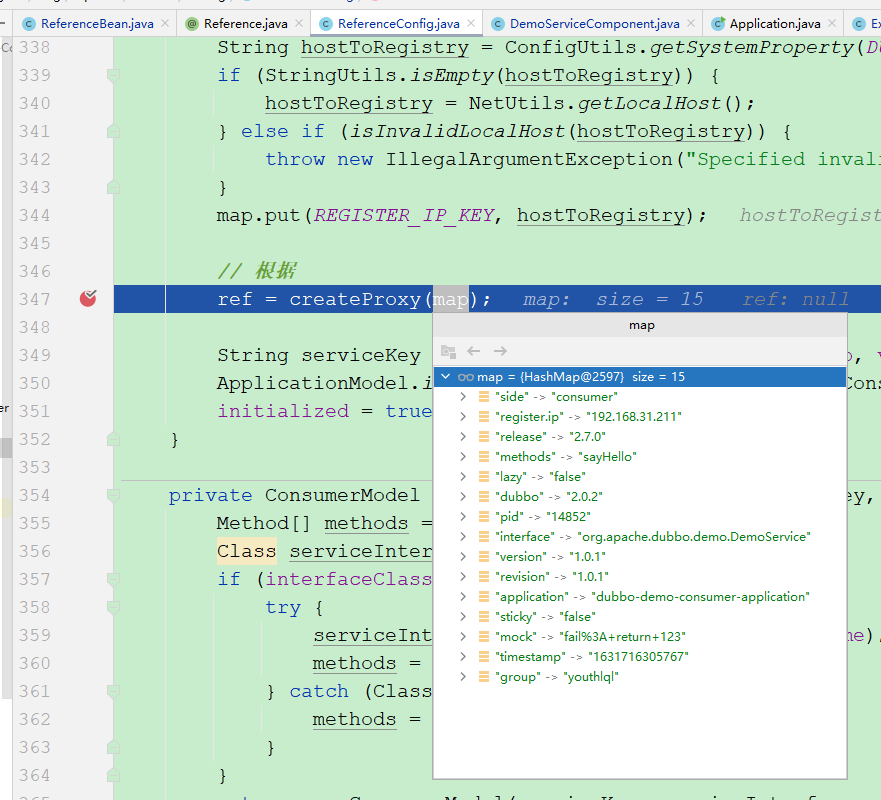
Dubbo官方给的Demo没有配置URL,所以这里就是NULL
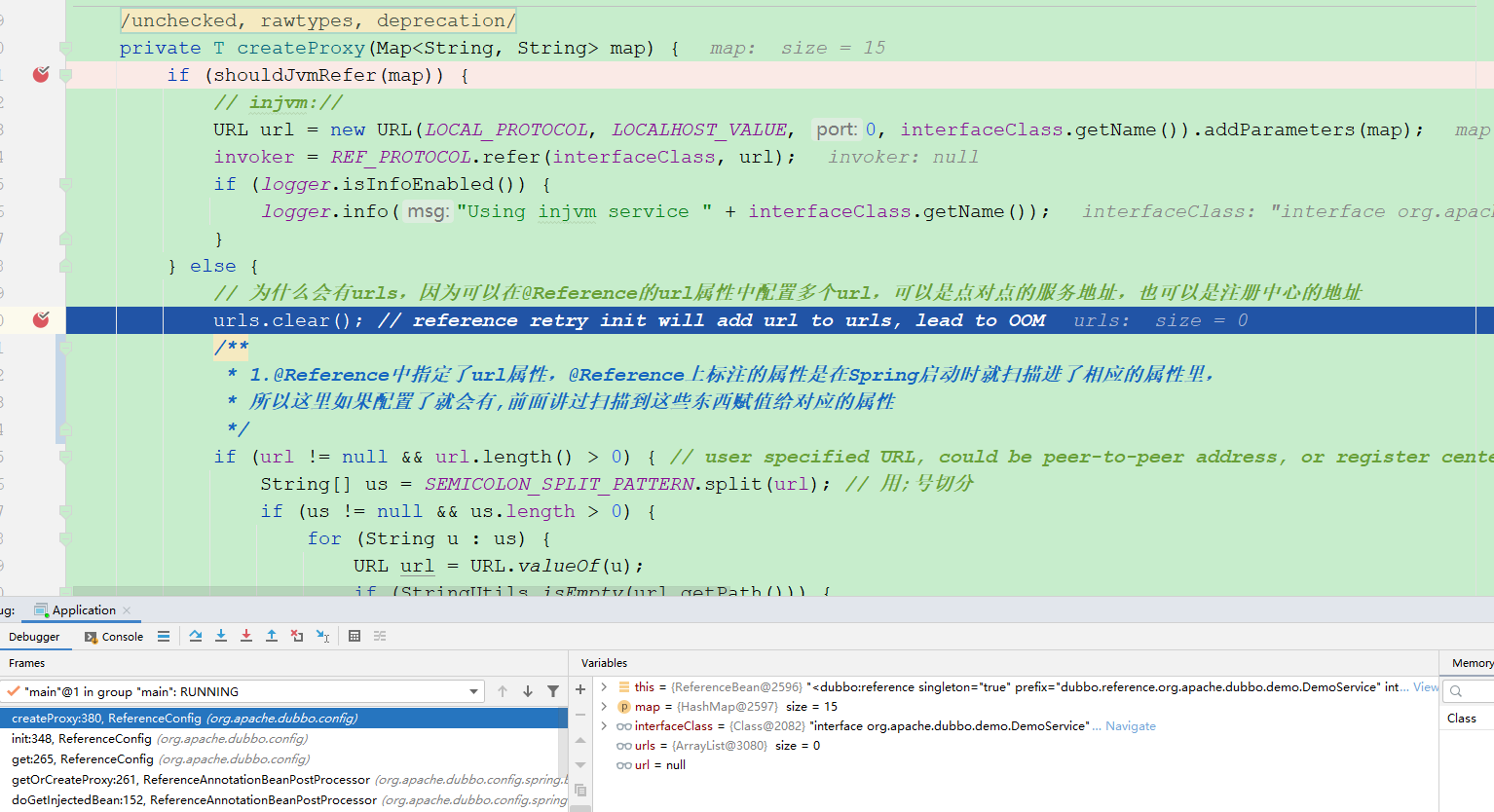
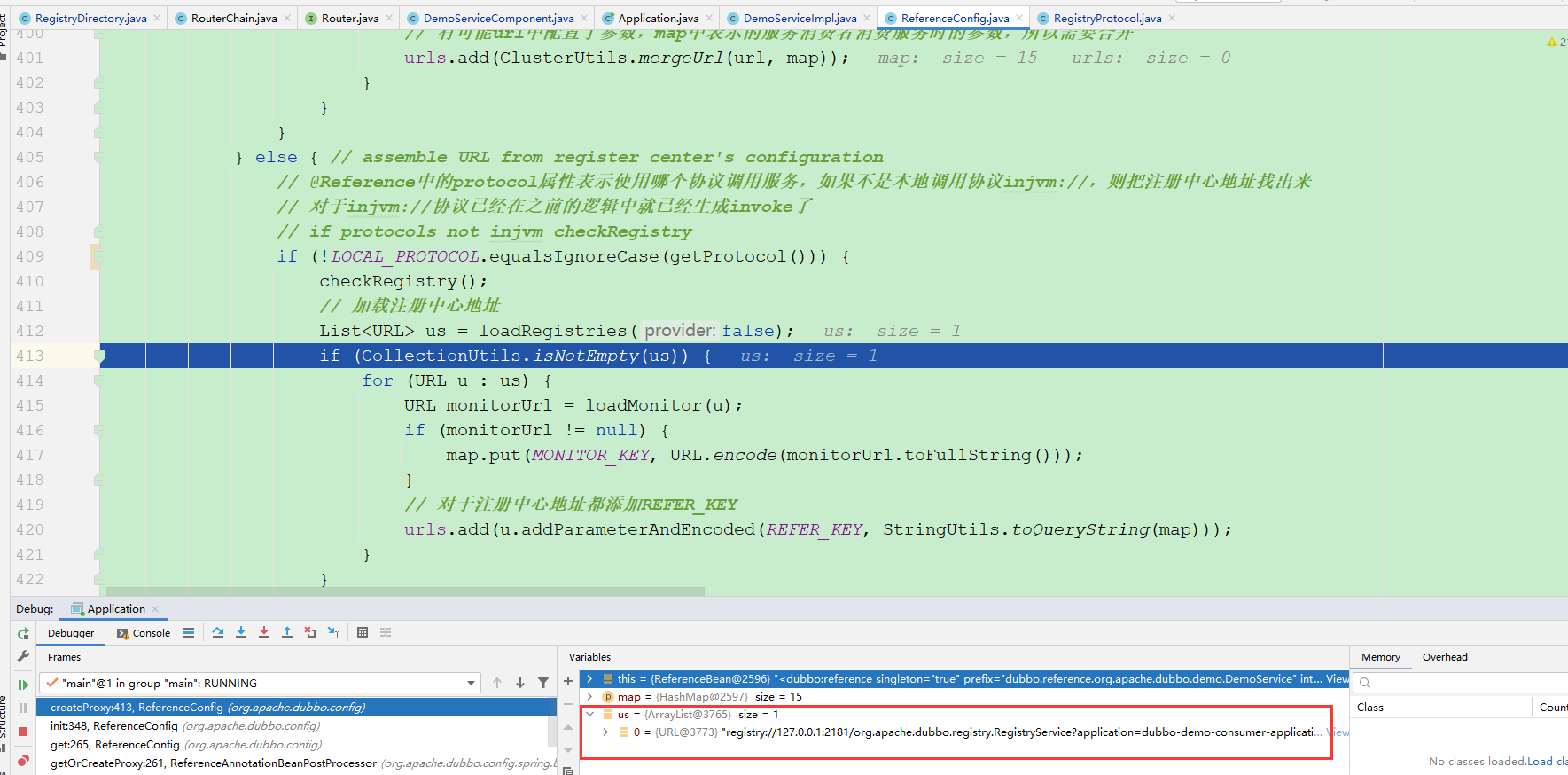
MockClusterWrapper
public class MockClusterWrapper implements Cluster {
private Cluster cluster;
public MockClusterWrapper(Cluster cluster) {
this.cluster = cluster;
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new MockClusterInvoker<T>(directory,
this.cluster.join(directory));
}
}
RegistryAwareCluster
public class RegistryAwareCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "registryaware";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new RegistryAwareClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
RegistryAwareClusterInvoker
public class RegistryAwareClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RegistryAwareClusterInvoker.class);
public RegistryAwareClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
// First, pick the invoker (XXXClusterInvoker) that comes from the local registry, distinguish by a 'default' key.
// 如果在引入服务时,存在多个invoker,并且某个invoker是default的,则在调用时会使用该invoker,不会调用其它invoker
//就比如说配置文件写了两个注册中心,然后会生成
/**
* 1.如果在引入服务时,存在多个invoker,并且某个invoker是default的,
* 则在调用时会使用该invoker,不会调用其它invoker
* 2.比如说配置文件写了两个注册中心,一个redis和一个zookeeper
*/
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
if (invoker.isAvailable() && invoker.getUrl().getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + DEFAULT_KEY, false)) {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
// If none of the invokers has a local signal, pick the first one available.
// 如果没有default,则取第一个
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
// 如果对应的注册中心中没有当前调用的服务信息,则不可用
if (invoker.isAvailable()) {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers);
}
}
源码分析-监听注册中心并第一次拉取provider配置
RegistryProtocol
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
// 从registry://的url中获取对应的注册中心,比如zookeeper
// url由 registry:// 改变为---> zookeeper://
url = URLBuilder.from(url)
.setProtocol(url.getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY, DEFAULT_REGISTRY))
.removeParameter(REGISTRY_KEY)
.build();
// 拿到注册中心实现,ZookeeperRegistry
Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url);
// 下面这个代码,通过过git历史提交记录是用来解决SimpleRegistry不可用的问题,不用管这里
if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) {
return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url);
}
// qs表示 queryString, 表示url中的参数,表示消费者引入服务时@Reference所配置的参数
// 就是把URL中的参数变成kv形式的map
Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(REFER_KEY));
// group="a,b" or group="*"
// https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/examples/group-merger/
String group = qs.get(GROUP_KEY);
if (group != null && group.length() > 0) {
if ((COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1 || "*".equals(group)) {
// group有多个值,这里的cluster为MergeableCluster
return doRefer(getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url);
}
}
// 这里的cluster是cluster的Adaptive对象,扩展点
return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url);
}
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// RegistryDirectory表示动态服务目录,会和注册中心的数据保持同步
// type表示一个服务对应一个RegistryDirectory,url表示注册中心地址
// 在消费端,最核心的就是RegistryDirectory
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
// all attributes of REFER_KEY
// 引入服务所配置的参数
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters());
// 消费者url
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters);
if (!ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface()) && url.getParameter(REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
directory.setRegisteredConsumerUrl(getRegisteredConsumerUrl(subscribeUrl, url));
// 注册简化后的消费url
registry.register(directory.getRegisteredConsumerUrl());
}
// 构造路由链,路由链会在引入服务时按路由条件进行过滤
// 路由链是动态服务目录中的一个属性,通过路由链可以过滤某些服务提供者
directory.buildRouterChain(subscribeUrl);
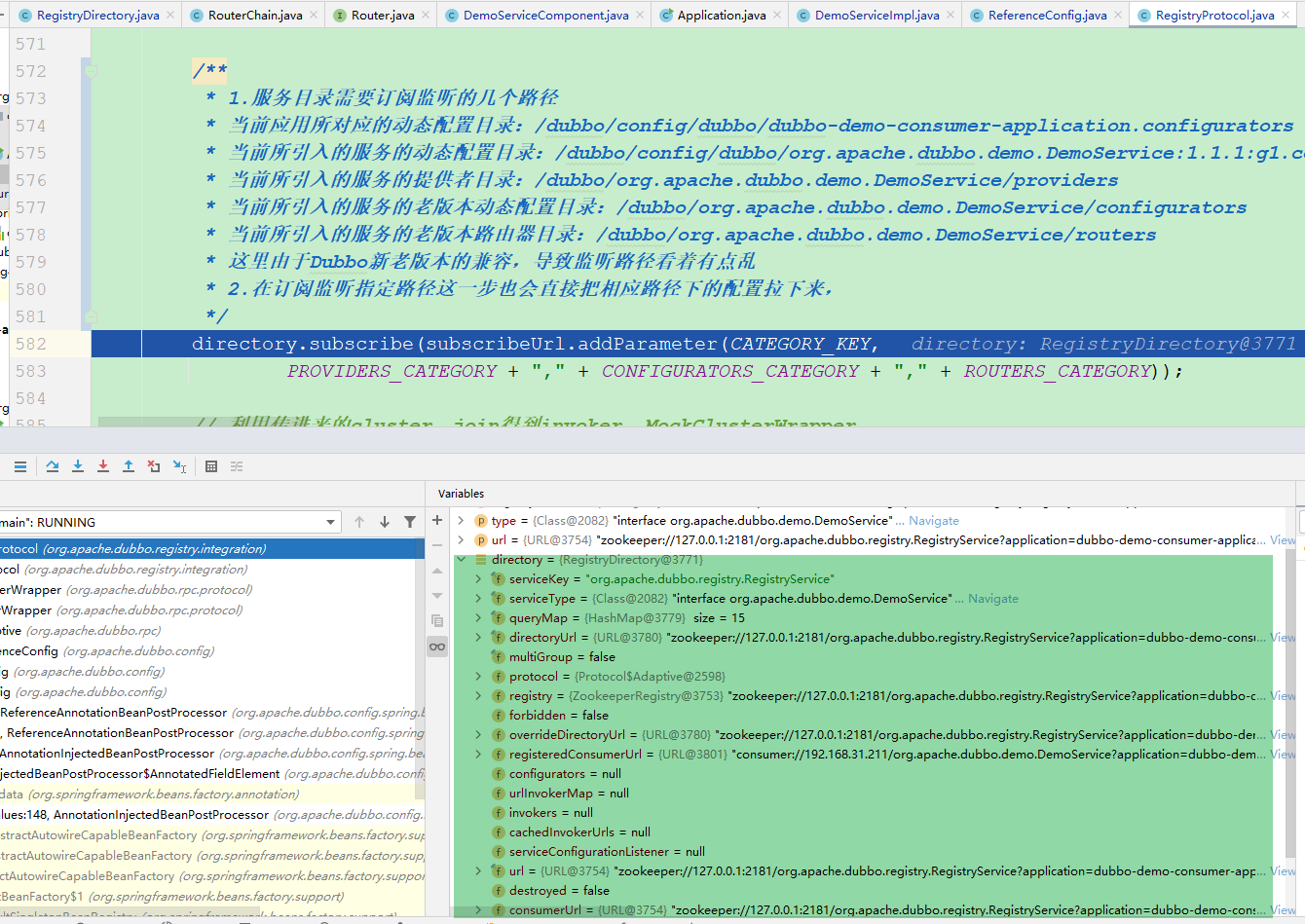
/**
* 1.服务目录需要订阅监听的几个路径
* 当前应用所对应的动态配置目录:/dubbo/config/dubbo/dubbo-demo-consumer-application.configurators
* 当前所引入的服务的动态配置目录:/dubbo/config/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService:1.1.1:g1.configurators
* 当前所引入的服务的提供者目录:/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/providers
* 当前所引入的服务的老版本动态配置目录:/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators
* 当前所引入的服务的老版本路由器目录:/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/routers
* 这里由于Dubbo新老版本的兼容,导致监听路径看着有点乱
* 2.在订阅监听指定路径这一步也会直接把相应路径下的配置拉下来,
*/
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(CATEGORY_KEY,
PROVIDERS_CATEGORY + "," + CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY + "," + ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
// 利用传进来的cluster,join得到invoker, MockClusterWrapper
Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory);
return invoker;
}
RegistryDirectory
public void subscribe(URL url) {
setConsumerUrl(url);
CONSUMER_CONFIGURATION_LISTENER.addNotifyListener(this); // 监听consumer应用
serviceConfigurationListener = new ReferenceConfigurationListener(this, url); // 监听所引入的服务的动态配置
// 这里又是SPI,会先调用FailbackRegistry
registry.subscribe(url, this);
}
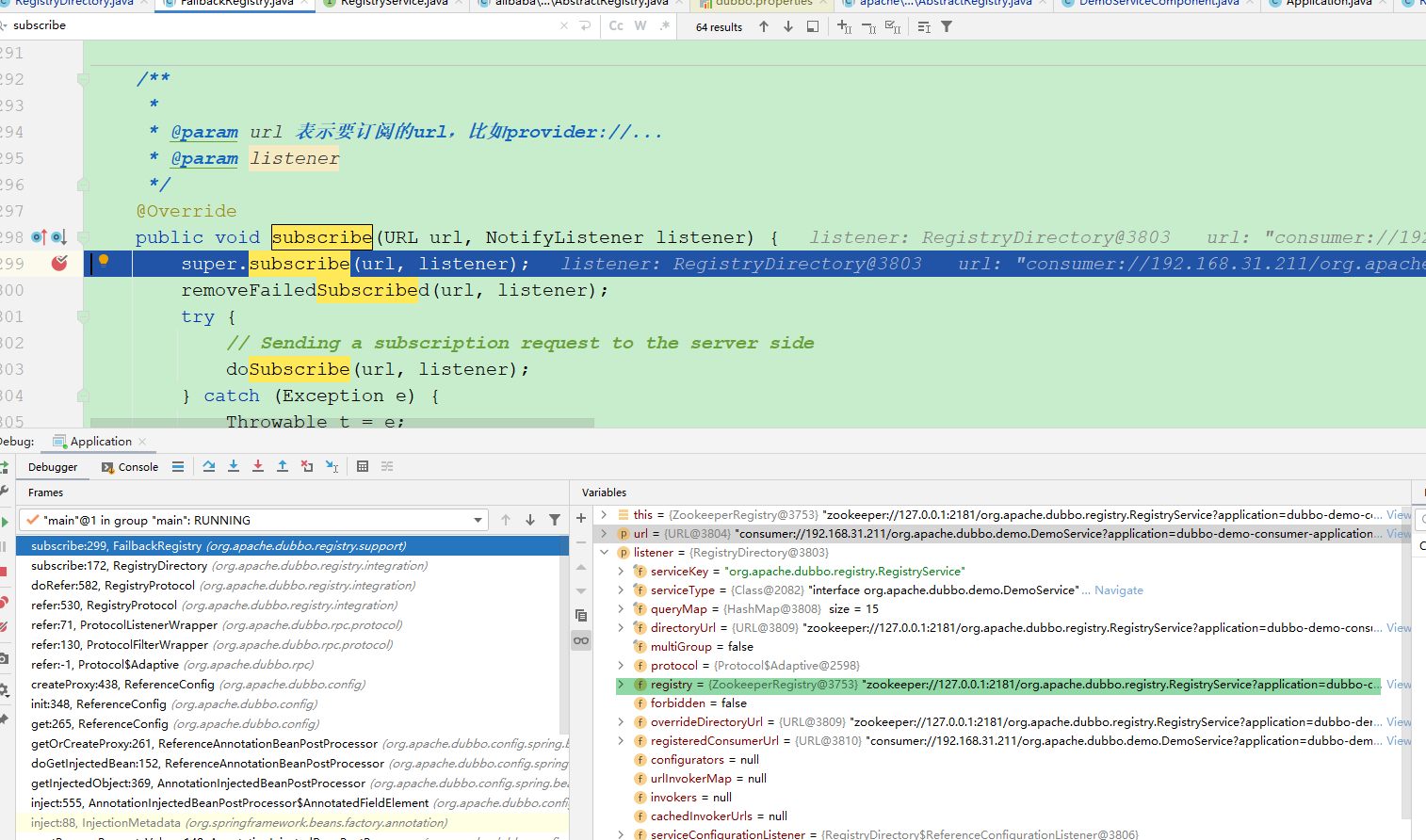
- 这里再讲一下,为什么这里会先调用FailbackRegistry。
- 这里的SPI机制是根据this对象的registry属性来决定的,this是RegistryDirectory对象,RegistryDirectory实现了NotifyListener接口
- 看下面的截图,registry属性是zookeeper的URL,所以应该是要调用ZookeeperRegistry的subscribe()方法,但是ZookeeperRegistry没有这个方法,所以我们就要找它的父类了,也就是FailbackRegistry,
- 然后再调用doSubscribe(),ZookeeperRegistry重写了此方法,很明显这是个模板模式。
FailbackRegistry
public void subscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener) {
super.subscribe(url, listener);
removeFailedSubscribed(url, listener);
try {
// Sending a subscription request to the server side
doSubscribe(url, listener);
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e;
List<URL> urls = getCacheUrls(url);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(urls)) {
notify(url, listener, urls);
logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", Using cached list: " + urls + " from cache file: " + getUrl().getParameter(FILE_KEY, System.getProperty("user.home") + "/dubbo-registry-" + url.getHost() + ".cache") + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
} else {
// If the startup detection is opened, the Exception is thrown directly.
boolean check = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true)
&& url.getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true);
boolean skipFailback = t instanceof SkipFailbackWrapperException;
if (check || skipFailback) {
if (skipFailback) {
t = t.getCause();
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
} else {
logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
// Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly
// 添加listener,向zk添加监听器时如果报错了,那么会把这个listener添加到failedSubscribed中,并会定时重试(重新注册listener)
addFailedSubscribed(url, listener);
}
}
ZookeeperRegistry
// 进行订阅,先看父类的subscribe方法
@Override
public void doSubscribe(final URL url, final NotifyListener listener) {
try {
if (ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
// 订阅所有服务
String root = toRootPath();
ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
if (listeners == null) {
zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
}
ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
if (zkListener == null) {
listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, (parentPath, currentChilds) -> {
for (String child : currentChilds) {
child = URL.decode(child);
if (!anyServices.contains(child)) {
anyServices.add(child);
subscribe(url.setPath(child).addParameters(INTERFACE_KEY, child,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener);
}
}
});
zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
}
zkClient.create(root, false);
List<String> services = zkClient.addChildListener(root, zkListener);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(services)) {
for (String service : services) {
service = URL.decode(service);
anyServices.add(service);
subscribe(url.setPath(service).addParameters(INTERFACE_KEY, service,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener);
}
}
} else {
// 单独订阅某一个服务
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<>();
// 得到真正要监听的zk上的路径,
for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) {
// 根据监听地址去拿listeners,如果没有则生成
ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
if (listeners == null) {
zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
}
// 一个NotifyListener对应一个ChildListener
ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
if (zkListener == null) {
// lambda表达式就是监听逻辑, parentPath表示父path,currentChilds表示当前拥有的child, 会调用notify方法进行实际的处理
listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, (parentPath, currentChilds) -> ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, listener, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds)));
zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
}
// 创建zk上路径
zkClient.create(path, false);
// 添加真正跟zk相关的ChildListener,ChildListener中的逻辑就是监听到zk上数据发生了变化后会触发的逻辑
List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener);
if (children != null) {
urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children));
}
}
// 这里的urls就是从现在所引入的服务的目录下先主动拉一次配置,比如下面这个三个目录下的路径
// "/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/providers"
// "/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators"
// "/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/routers"
notify(url, listener, urls);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to subscribe " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
FailbackRegistry
这里再调用父类的通知方法,先主动把注册中心上的配置拉下来一次
/**
* 接收到通知,处理通知的方法
* @param url 被监听的url
* @param listener 监听器
* @param urls 要么有一个empty://,要么有一个或多个override://协议
*/
@Override
protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify url == null");
}
if (listener == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify listener == null");
}
try {
doNotify(url, listener, urls);
} catch (Exception t) {
// 处理通知失败
// Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly
addFailedNotified(url, listener, urls);
logger.error("Failed to notify for subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
protected void doNotify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
super.notify(url, listener, urls);
}
AbstractRegistry
protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify url == null");
}
if (listener == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify listener == null");
}
if ((CollectionUtils.isEmpty(urls))
&& !ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
logger.warn("Ignore empty notify urls for subscribe url " + url);
return;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Notify urls for subscribe url " + url + ", urls: " + urls);
}
// keep every provider's category.
Map<String, List<URL>> result = new HashMap<>();
for (URL u : urls) {
if (UrlUtils.isMatch(url, u)) {
String category = u.getParameter(CATEGORY_KEY, DEFAULT_CATEGORY);
List<URL> categoryList = result.computeIfAbsent(category, k -> new ArrayList<>());
categoryList.add(u);
}
}
if (result.size() == 0) {
return;
}
Map<String, List<URL>> categoryNotified = notified.computeIfAbsent(url, u -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
for (Map.Entry<String, List<URL>> entry : result.entrySet()) {
String category = entry.getKey();
List<URL> categoryList = entry.getValue();
categoryNotified.put(category, categoryList);
//从这里进
listener.notify(categoryList);
// We will update our cache file after each notification.
// When our Registry has a subscribe failure due to network jitter, we can return at least the existing cache URL.
saveProperties(url);
}
}
最终走到了这一步
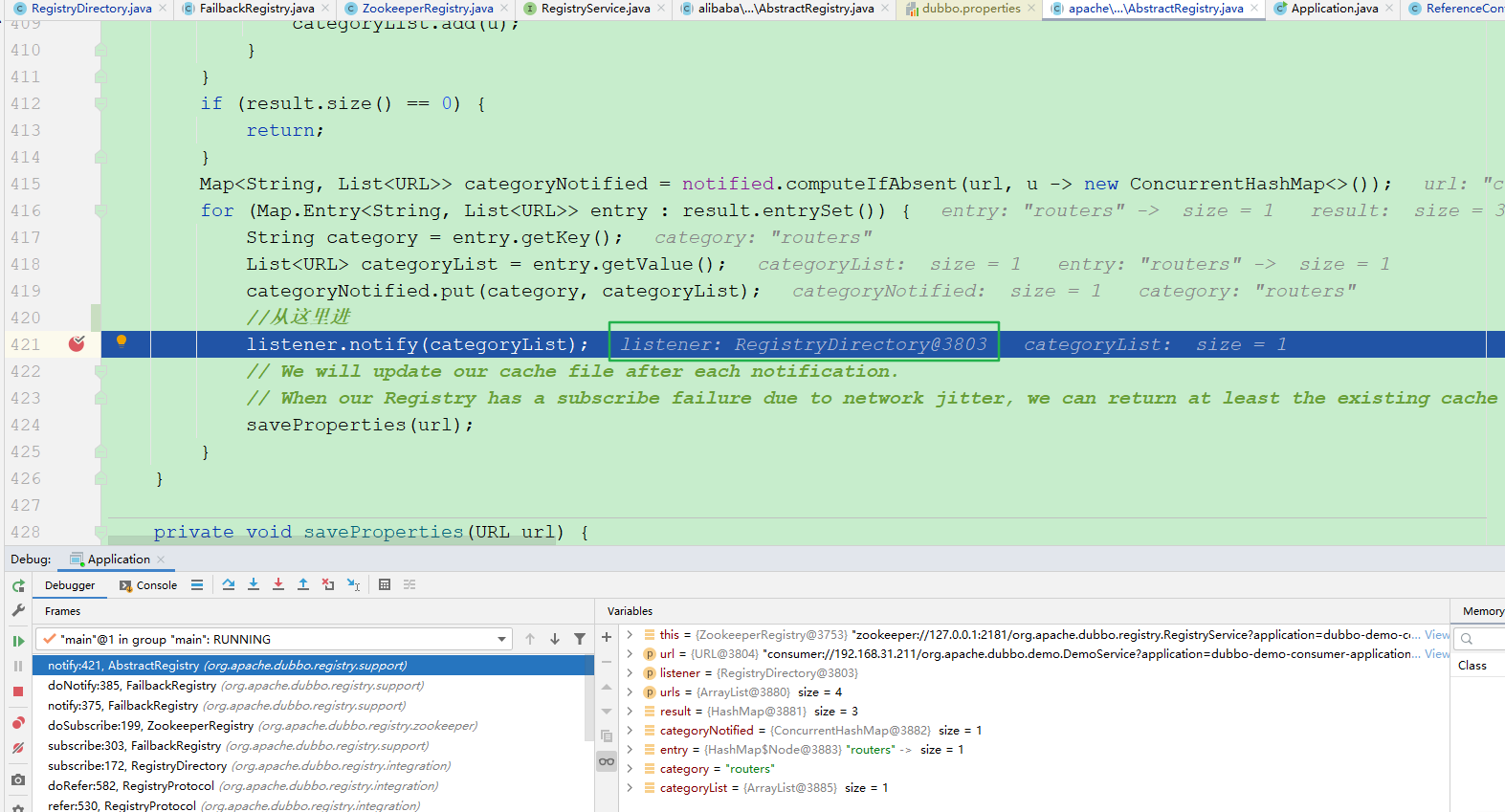
RegistryDirectory
public synchronized void notify(List<URL> urls) {
Map<String, List<URL>> categoryUrls = urls.stream()
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.filter(this::isValidCategory)
.filter(this::isNotCompatibleFor26x)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(url -> {
if (UrlUtils.isConfigurator(url)) {
return CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY;
} else if (UrlUtils.isRoute(url)) {
return ROUTERS_CATEGORY;
} else if (UrlUtils.isProvider(url)) {
return PROVIDERS_CATEGORY;
}
return "";
}));
// 获取动态配置URL,生成configurators
List<URL> configuratorURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList());
this.configurators = Configurator.toConfigurators(configuratorURLs).orElse(this.configurators);
// 获取老版本路由URL,生成Router,并添加到路由链中
List<URL> routerURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(ROUTERS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList());
toRouters(routerURLs).ifPresent(this::addRouters);
// 获取服务提供者URL
List<URL> providerURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(PROVIDERS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList());
refreshOverrideAndInvoker(providerURLs);
}
private void refreshOverrideAndInvoker(List<URL> urls) {
// mock zookeeper://xxx?mock=return null
overrideDirectoryUrl();
refreshInvoker(urls);
}
private void refreshInvoker(List<URL> invokerUrls) { //http:// dubbo://
Assert.notNull(invokerUrls, "invokerUrls should not be null");
if (invokerUrls.size() == 1 && invokerUrls.get(0) != null && EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(invokerUrls.get(0).getProtocol())) {
this.forbidden = true; // Forbid to access
this.invokers = Collections.emptyList();
routerChain.setInvokers(this.invokers);
destroyAllInvokers(); // Close all invokers
} else {
this.forbidden = false; // Allow to access
Map<String, Invoker<T>> oldUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
if (invokerUrls == Collections.<URL>emptyList()) {
invokerUrls = new ArrayList<>();
}
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty() && this.cachedInvokerUrls != null) {
invokerUrls.addAll(this.cachedInvokerUrls);
} else {
this.cachedInvokerUrls = new HashSet<>();
this.cachedInvokerUrls.addAll(invokerUrls);//Cached invoker urls, convenient for comparison
}
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 这里会先按Protocol进行过滤,并且调用DubboProtocol.refer方法得到DubboInvoker
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls);// Translate url list to Invoker map
/**
* If the calculation is wrong, it is not processed.
*
* 1. The protocol configured by the client is inconsistent with the protocol of the server.
* eg: consumer protocol = dubbo, provider only has other protocol services(rest).
* 2. The registration center is not robust and pushes illegal specification data.
*
*/
if (CollectionUtils.isEmptyMap(newUrlInvokerMap)) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("urls to invokers error .invokerUrls.size :" + invokerUrls.size() + ", invoker.size :0. urls :" + invokerUrls
.toString()));
return;
}
List<Invoker<T>> newInvokers = Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<>(newUrlInvokerMap.values()));
// pre-route and build cache, notice that route cache should build on original Invoker list.
// toMergeMethodInvokerMap() will wrap some invokers having different groups, those wrapped invokers not should be routed.
// 得到了所引入的服务Invoker之后,把它们设置到路由链中去,在调用时使用,并且会调用TagRouter的notify方法
routerChain.setInvokers(newInvokers);
this.invokers = multiGroup ? toMergeInvokerList(newInvokers) : newInvokers;
this.urlInvokerMap = newUrlInvokerMap;
try {
destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap); // Close the unused Invoker
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("destroyUnusedInvokers error. ", e);
}
}
}
private Map<String, Invoker<T>> toInvokers(List<URL> urls) {
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = new HashMap<>();
if (urls == null || urls.isEmpty()) {
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
String queryProtocols = this.queryMap.get(PROTOCOL_KEY);
// 遍历当前服务所有的服务提供者URL
for (URL providerUrl : urls) {
// If protocol is configured at the reference side, only the matching protocol is selected
if (queryProtocols != null && queryProtocols.length() > 0) {
boolean accept = false;
String[] acceptProtocols = queryProtocols.split(",");
// 当前消费者如果手动配置了Protocol,那么则进行匹配
for (String acceptProtocol : acceptProtocols) {
if (providerUrl.getProtocol().equals(acceptProtocol)) {
accept = true;
break;
}
}
if (!accept) {
continue;
}
}
if (EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
continue;
}
// 当前Protocol是否在应用中存在对应的扩展点
if (!ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("Unsupported protocol " + providerUrl.getProtocol() +
" in notified url: " + providerUrl + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() +
" to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + ", supported protocol: " +
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getSupportedExtensions()));
continue;
}
//重要
URL url = mergeUrl(providerUrl);
String key = url.toFullString(); // The parameter urls are sorted
if (keys.contains(key)) { // Repeated url
continue;
}
keys.add(key);
// Cache key is url that does not merge with consumer side parameters, regardless of how the consumer combines parameters, if the server url changes, then refer again
Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
Invoker<T> invoker = localUrlInvokerMap == null ? null : localUrlInvokerMap.get(key);
// 如果当前服务提供者URL没有生产过Invoker
if (invoker == null) { // Not in the cache, refer again
try {
boolean enabled = true;
if (url.hasParameter(DISABLED_KEY)) {
enabled = !url.getParameter(DISABLED_KEY, false);
} else {
enabled = url.getParameter(ENABLED_KEY, true);
}
if (enabled) {
// 调用Protocol的refer方法得到一个Invoker DubboProtocol.refer()
invoker = new InvokerDelegate<>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to refer invoker for interface:" + serviceType + ",url:(" + url + ")" + t.getMessage(), t);
}
if (invoker != null) { // Put new invoker in cache
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
} else {
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
}
keys.clear();
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
// 这里就是根据优先级,把动态配置和服务提供者URL等等还有其它一些配置URL合并,得到真正能转换成DubboInvoker的URL
private URL mergeUrl(URL providerUrl) {
providerUrl = ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(providerUrl, queryMap); // Merge the consumer side parameters
//动态配置的内容去覆盖
providerUrl = overrideWithConfigurator(providerUrl);
providerUrl = providerUrl.addParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)); // Do not check whether the connection is successful or not, always create Invoker!
// The combination of directoryUrl and override is at the end of notify, which can't be handled here
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = this.overrideDirectoryUrl.addParametersIfAbsent(providerUrl.getParameters()); // Merge the provider side parameters
if ((providerUrl.getPath() == null || providerUrl.getPath()
.length() == 0) && DUBBO_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) { // Compatible version 1.0
//fix by tony.chenl DUBBO-44
String path = directoryUrl.getParameter(INTERFACE_KEY);
if (path != null) {
int i = path.indexOf('/');
if (i >= 0) {
path = path.substring(i + 1);
}
i = path.lastIndexOf(':');
if (i >= 0) {
path = path.substring(0, i);
}
providerUrl = providerUrl.setPath(path);
}
}
return providerUrl;
}
源码分析-路由链生成
构造路由链概述
- RouterChain.buildChain(url)方法赋值得到路由链。这里的url是这样的:
consumer://192.168.0.100/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?application=dubbo-demo-consumer-application
&dubbo=2.0.2&group=g1&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&lazy=false&methods=sayHello&pid=19852
&release=2.7.0&revision=1.1.1&side=consumer&sticky=false×tamp=1591332529643&version=1.1.1
- 表示所引入的服务的参数,在获得路由链时就要根据这些参数去匹配得到符合当前的服务的Router.
大致源码过程:
-
RouterChain.buildChain(url)
-
new RouterChain<>(url)
-
List
extensionFactories = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RouterFactory.class).getActivateExtension(url, (String[]) null);根据url去获取可用的RouterFactory,可以拿到四个: - MockRouterFactory:Mock路由,没有order,相当于order=0
- TagRouterFactory: 标签路由,order = 100
- AppRouterFactory: 应用条件路由,order = 200
- ServiceRouterFactory: 服务条件路由,order = 300
-
遍历每个RouterFactory,调用getRouter(url)方法得到Router,存到List
routers中 -
对routers按order从小到大的顺序进行排序
文字描述:
-
AppRouter和ServiceRouter是非常类似,他们的父类都是ListenableRouter,在创建AppRouter和ServiceRouter时,会绑定一个监听器,比如:
- AppRouter监听的是:/dubbo/config/dubbo/dubbo-demo-consumer-application.condition-router节点的内容
- ServiceRouter监听的是:/dubbo/config/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService:1.1.1:g1.condition-router节点的内容
-
绑定完监听器之后,会主动去获取一下对应节点的内容(也就是所配置的路由规则内容),然后会去解析内容得到ConditionRouterRule routerRule,再调用generateConditions(routerRule);方法解析出一个或多个ConditionRouter,并存入到List
conditionRouters中。 -
注意routerRule和conditionRouters是ListenableRouter的属性,就是在AppRouter和ServiceRouter中的。
-
对于TagRouter就比较特殊,首先标签路由是用在,当消费者在调用某个服务时,通过在请求中设置标签,然后根据所设置的标签获得可用的服务提供者地址。而且目前TagRouter只支持应用级别的配置(而且是服务提供者应用,给某个服务提供者应用打标)。
-
所以对于服务消费者而言,在引用某个服务时,需要知道提供这个服务的应用名,然后去监听这个应用名对应的.tag-router节点内容,比如/dubbo/config/dubbo/dubbo-demo-provider-application.tag-router。
-
那么问题来了,怎么才能知道提供这个服务的服务提供者的应用名呢?答案是,需要先获取到当前所引入服务的服务提供者URL,从URL中得到服务提供者的应用名。拿到应用名之后才能去应用名对应的.tag-router节点去绑定监听器。
-
这就是TagRouter和AppRouter、ServiceRouter的区别,对于AppRouter而言,监听的是本消费者应用的路由规则,对于ServiceRouter而言,监听的是所引入服务的路由规则,都比较简单。
-
所以,TagRouter是在引入服务时,获取到服务的提供者URL之后,才会去监听.tag-router节点中的内容,并手动获取一次节点中的内容,设置TagRouter对象中tagRouterRule属性,表示标签路由规则。
到此,路由链构造完毕。
RegistryProtocol
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// RegistryDirectory表示动态服务目录,会和注册中心的数据保持同步
// type表示一个服务对应一个RegistryDirectory,url表示注册中心地址
// 在消费端,最核心的就是RegistryDirectory
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
// all attributes of REFER_KEY
// 引入服务所配置的参数
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters());
// 消费者url
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters);
if (!ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface()) && url.getParameter(REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
directory.setRegisteredConsumerUrl(getRegisteredConsumerUrl(subscribeUrl, url));
// 注册简化后的消费url
registry.register(directory.getRegisteredConsumerUrl());
}
// 构造路由链,路由链会在引入服务时按路由条件进行过滤
// 路由链是动态服务目录中的一个属性,通过路由链可以过滤某些服务提供者
directory.buildRouterChain(subscribeUrl);
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(CATEGORY_KEY,
PROVIDERS_CATEGORY + "," + CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY + "," + ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
// 利用传进来的cluster,join得到invoker, MockClusterWrapper
Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory);
return invoker;
}
RegistryDirectory
public void buildRouterChain(URL url) {
this.setRouterChain(RouterChain.buildChain(url));
}
RouterChain
public static <T> RouterChain<T> buildChain(URL url) {
return new RouterChain<>(url);
}
private RouterChain(URL url) {
// 拿到RouterFactory接口有哪些扩展实现类,比如默认情况下就有四个:
// 0 = {MockRouterFactory@2880}
// 1 = {TagRouterFactory@2881} // 标签路由
// 2 = {AppRouterFactory@2882} // 应用条件路由
// 3 = {ServiceRouterFactory@2883} // 服务条件路由
List<RouterFactory> extensionFactories = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RouterFactory.class)
.getActivateExtension(url, (String[]) null);
// 然后利用RouterFactory根据url生成各个类型的Router
// 这里生产的routers已经是真实可用的了,但是有个比较特殊的:
// 对于应用条件路由和服务条件路由对于的Router对象,对象内部已经有真实可用的数据了(数据已经从配置中心得到了)
// 但是对于标签路由则没有,它暂时还相当于一个没有内容的对象(还没有从配置中心获取标签路由的数据)
List<Router> routers = extensionFactories.stream()
.map(factory -> factory.getRouter(url))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 把routers按priority进行排序
initWithRouters(routers);
}
public void setInvokers(List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
this.invokers = (invokers == null ? Collections.emptyList() : invokers);
routers.forEach(router -> router.notify(this.invokers));
}
AppRouterFactory
以AppRouterFactory为例
@Activate(order = 200)
public class AppRouterFactory implements RouterFactory {
public static final String NAME = "app";
private volatile Router router;
@Override
public Router getRouter(URL url) {
if (router != null) {
return router;
}
synchronized (this) {
if (router == null) {
router = createRouter(url);
}
}
return router;
}
private Router createRouter(URL url) {
// 内部会进行初始化
return new AppRouter(DynamicConfiguration.getDynamicConfiguration(), url);
}
}
AppRouter
public class AppRouter extends ListenableRouter {
public static final String NAME = "APP_ROUTER";
/**
* AppRouter should after ServiceRouter
*/
private static final int APP_ROUTER_DEFAULT_PRIORITY = 150;
public AppRouter(DynamicConfiguration configuration, URL url) {
// 拿到应用名
super(configuration, url, url.getParameter(CommonConstants.APPLICATION_KEY));
this.priority = APP_ROUTER_DEFAULT_PRIORITY;
}
}
ListenableRouter
public ListenableRouter(DynamicConfiguration configuration, URL url, String ruleKey) {
super(configuration, url);
this.force = false;
// ruleKey为服务名或应用名
// 初始化,会绑定一个监听器,负责监听配置中心条件路由的修改,并且会主动从配置中心获取一下当前条件路由的数据并做解析
this.init(ruleKey);
}
private synchronized void init(String ruleKey) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(ruleKey)) {
return;
}
// 服务名+".condition-router",或 应用名+".condition-router"
String routerKey = ruleKey + RULE_SUFFIX;
// 绑定一个监听器去监听routerKey对应的路径,当前类ListenableRouter就自带了一个监听器
configuration.addListener(routerKey, this);
// 绑定完监听器后,主动的从配置中心获取一下当前服务或消费者应用的对应的路由配置
String rule = configuration.getRule(routerKey, DynamicConfiguration.DEFAULT_GROUP);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(rule)) {
// 手动调用监听器处理事件的方法process()
this.process(new ConfigChangeEvent(routerKey, rule));
}
}
public synchronized void process(ConfigChangeEvent event) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Notification of condition rule, change type is: " + event.getChangeType() +
", raw rule is:\n " + event.getValue());
}
if (event.getChangeType().equals(ConfigChangeType.DELETED)) {
// 如果是一个删除事件,则清空当前Router中的conditionRouters属性,表示当前Router对象中没有路由规则
routerRule = null;
conditionRouters = Collections.emptyList();
} else {
try {
// 解析路由规则
routerRule = ConditionRuleParser.parse(event.getValue());
// 根据路由规则,生成ConditionRouter-条件路由对象,并赋值给当前Router对象的conditionRouters属性
generateConditions(routerRule);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Failed to parse the raw condition rule and it will not take effect, please check " +
"if the condition rule matches with the template, the raw rule is:\n " + event.getValue(), e);
}
}
}
Invoker总结
MockClusterInvoker: 完成Mock功能,由MockClusterWrapper生成,MockClusterWrapper是Cluster接口的包装类,通过Cluster.join()方法得到MockClusterInvoker
FailoverClusterInvoker:完成集群容错功能,是MockClusterInvoker的下级
RegistryAwareClusterInvoker:如果指定了多个注册中心,那么RegistryAwareClusterInvoker完成选择默认的注册中心的进行调用,如果没有指定默认的,则会遍历注册中心进行调用,如果该注册中心没有对应的服务则跳过。
DubboInvoker:完成Dubbo协议底层发送数据
ProtocolFilterWrapper$CallbackRegistrationInvoker:完成对filter的调用,ProtocolFilterWrapper是Protocol接口的包装类,通过Protocol.refer()方法得到CallbackRegistrationInvoke。
DubboProtocol的服务引入(Refer)
DubboProtocol中并没有refer方法,是在它的父类AbstractProtocol中才有的refer方法
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
// 异步转同步Invoker , type是接口,url是服务地址
// DubboInvoker是异步的,而AsyncToSyncInvoker会封装为同步的
return new AsyncToSyncInvoker<>(protocolBindingRefer(type, url));
}
调用protocolBindingRefer()方法得到一个Invoker后,会包装为一个AsyncToSyncInvoker然后作为refer方法的结果返回。
在DubboProtocol的protocolBindingRefer()方法中会new一个DubboInvoker,然后就返回了。
在构造DubboInvoker时,有一个非常重要的步骤,构造clients。DubboInvoker作为消费端服务的执行者,在调用服务时,是需要去发送Invocation请求的,而发送请求就需要client,之所以有多个client,是因为DubboProtocol支持多个。
假如在一个DubboInvoker中有多个Client,那么在使用这个DubboInvoker去调用服务时,就可以提高效率,比如一个服务接口有多个方法,那么在业务代码中,可能会不断的调用该接口中的方法,并且由于DubboProtocol底层会使用异步去发送请求,所以在每次需要发送请求时,就可以从clients轮询一个client去发送这个数据,从而提高效率。
接下来,来看看clients是如何生成的。
-
首先,一个DubboInvoker到底支持多少个Client呢?这是可以配置的,参数为connections,按指定的数字调用initClient(url)得到ExchangeClient。
-
initClient(url)的实现逻辑为
- 获取client参数,表示是用netty还是mina等等
- 获取codec参数,表示数据的编码方式
- 获取****heartbeat参数,表示长连接的心跳时间,超过这个时间服务端没有收到数据则关闭socket,默认为1分钟
- 如果所指定的client没有对应的扩展点,则抛异常
- 获取lazy参数,默认为false,如果为true,那么则直接返回一个LazyConnectExchangeClient,表示真正在发送数据时才建立socket
- 否则调用Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler)获得一个client
- 在connect()方法中调用HeaderExchanger的connect方法去建立socket连接并得到一个HeaderExchangeClient
- 在构造HeaderExchangeClient时需要先执行Transporters.connect()方法得到一个Client
- 会调用NettyTransporter的connect()去构造一个NettyClient
- 在构造NettyClient的过程中,会去初始化Netty的客户端,然后连接Server端,建立一个Socket连接
最复杂情况下的Invoker链
@Reference(url = "dubbo://192.168.40.17:20881/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService;registry://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?registry=zookeeper")
private DemoService demoService;
在@Reference注解上定义了url参数,有两个值
- dubbo://192.168.40.17:20881/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService
- registry://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?registry=zookeeper
最终refer处理的invoker链路为:
-
MockClusterInvoker
-
invoker=RegistryAwareClusterInvoker
-
directory=StaticDirectory
-
0=ProtocolFilterWrapper$CallbackRegistrationInvoke子流程
-
1=MockClusterInvoker
-
FailoverClusterInvoker
-
RegistryDirectory
-
invokers=UnmodifiableRandomAccessList size=1
-
0=RegistryDirectory$InvokerDelegate
- ProtocolFilterWrapper$CallbackRegistrationInvoke子流程
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
ProtocolFilterWrapper$CallbackRegistrationInvoke子流程
-
filterInvoker=ProtocolFilterWrapper$1
-
filter=ConsumerContextFilter
-
next=ProtocolFilterWrapper$1
-
filter=FutureFilter
-
next=ProtocolFilterWrapper$1
-
filter=MonitorFilter
-
next=ListenerInvokerWrapper
- invoker=AsyncToSyncInvoker
- invoker=DubboInvoker
- invoker=AsyncToSyncInvoker
-
-
-
-
