Spring源码系列-第1章-Spring源码纵览
必读
- 源码是循循渐进的,前面我会省略中间很多目前不需要深入的代码,所以会看起来代码比较少。省略的地方我会打上这样的标识
// ...
或者
// ......
- 如果没打也不代表我没省略,可能是忘记了,不要看懵了。
第1章-Spring源码纵览
概述
Spring源码纵览这一节,主要是先了解下Spring的一些核心东西,所以前后可能关联不是特别深,跳跃性比较大,往后看就行。
简单的继承关系图
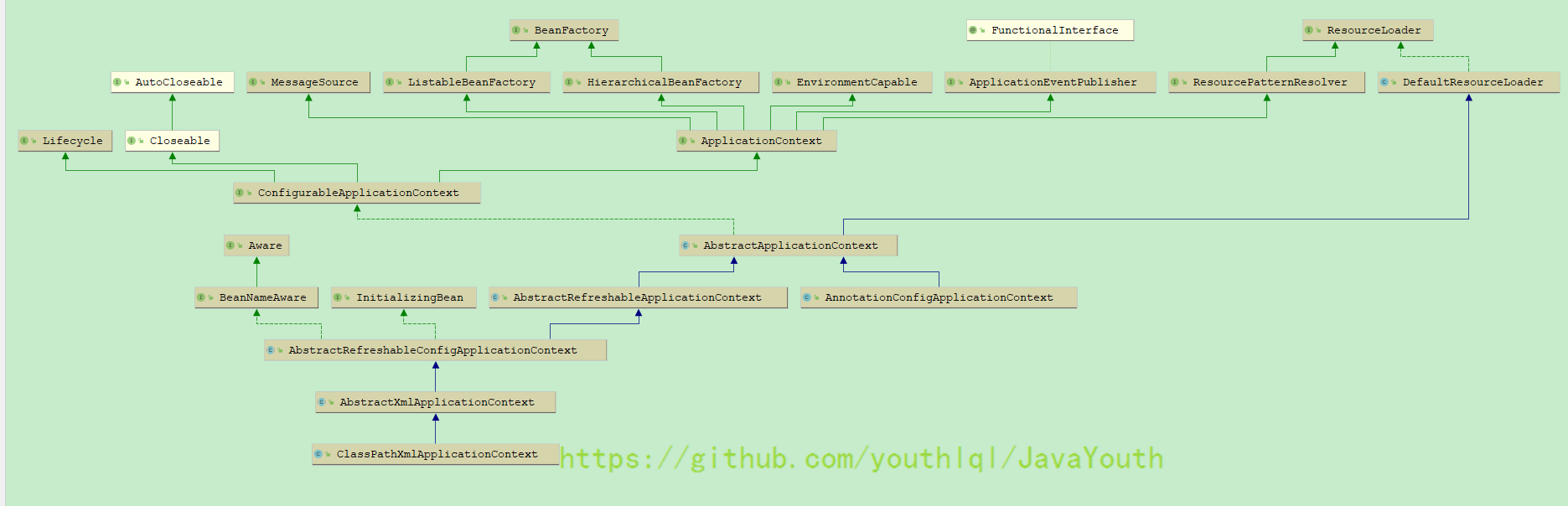
-
蓝色实线箭头是指继承关系
-
绿色虚线箭头是指接口实现关系
-
绿色虚线箭头是指接口继承关系
-
注解版使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
-
XML版使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
Spring框架整体流程
- 不管是用XML还是注解也好,最终形成一份组件或者功能的配置清单。
- Spring用Resource来表示所有的资源
- 这些资源被ResourceLoader加载然后交给BeanDefinitionReader解析成BeanDefinition(Bean的定义信息)。BeanDefinition就是一个对象的图纸,模板。
- 然后将这些BeanDefinition放入到BeanDefinitionRegistry(其实就是一个Map)里,等待以后使用。
- 最后经过漫长的过程,根据BeanDefinition创建一个个的对象。
核心组件接口分析
基础接口
Resource+ResourceLoader
BeanFactory
BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionReader
BeanDefinitionRegistry
ApplicationContext
Aware
生命周期-后置处理器
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
InitializingBean
BeanPostProcessor
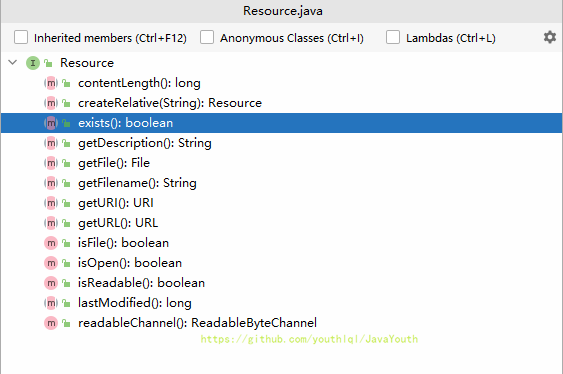
Resource资源
方法
快捷键:ctrl+F12 看类的方法
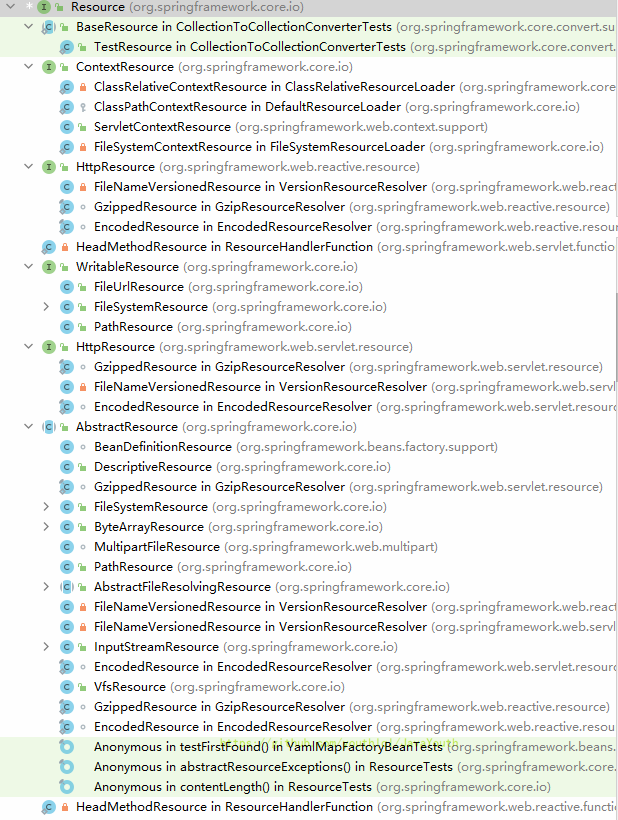
实现类
快捷键:ctrl+h 查看接口实现类
-
ContextResource:表示可以拿Web环境的资源
-
HttpResource:可以从网络中拿到资源
-
WritableResource:
- FileSystemResource:可以从文件系统拿到资源
- FileUrlResource:URL就是统一资源定位符的意思;URL可以定位到网络,磁盘,等任何你想定位到的位置;表示Spring几乎可以从任何地方拿到资源。
-
AbstractResource
- ByteArrayResource:从byte数组拿到资源
- InputStreamResource:从Input流中拿到资源
-
综合来说Spring几乎可以从任何地方拿到资源。
ResourceLoader资源加载器
此类的源码开头有这样一句话,Strategy interface(策略接口),显然用到了策略模式。策略体现在哪个地方,我们下面再说。
Strategy interface for loading resources (e.g., class path or file systemresources)
方法
/**
* Strategy interface(策略接口) for loading resources (e.g., class path or file system
* resources). An {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext}
* is required to provide this functionality plus extended
* {@link org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver} support.
*
* <p>{@link DefaultResourceLoader} is a standalone implementation that is
* usable outside an ApplicationContext and is also used by {@link ResourceEditor}.
*
* <p>Bean properties of type {@code Resource} and {@code Resource[]} can be populated
* from Strings when running in an ApplicationContext, using the particular
* context's resource loading strategy.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 10.03.2004
* @see Resource
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware
*/
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:". */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* Return a {@code Resource} handle for the specified resource location.
* <p>The handle should always be a reusable resource descriptor,
* allowing for multiple {@link Resource#getInputStream()} calls.
* <p><ul>
* <li>Must support fully qualified URLs, e.g. "file:C:/test.dat".
* <li>Must support classpath pseudo-URLs, e.g. "classpath:test.dat".
* <li>Should support relative file paths, e.g. "WEB-INF/test.dat".
* (This will be implementation-specific, typically provided by an
* ApplicationContext implementation.)
* </ul>
* <p>Note that a {@code Resource} handle does not imply an existing resource;
* you need to invoke {@link Resource#exists} to check for existence.
* @param location the resource location
* @return a corresponding {@code Resource} handle (never {@code null})
* @see #CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
* @see Resource#exists()
* @see Resource#getInputStream()
*/
Resource getResource(String location); //这个是最关键的
/**
* Expose the {@link ClassLoader} used by this {@code ResourceLoader}.
* <p>Clients which need to access the {@code ClassLoader} directly can do so
* in a uniform manner with the {@code ResourceLoader}, rather than relying
* on the thread context {@code ClassLoader}.
* @return the {@code ClassLoader}
* (only {@code null} if even the system {@code ClassLoader} isn't accessible)
* @see org.springframework.util.ClassUtils#getDefaultClassLoader()
* @see org.springframework.util.ClassUtils#forName(String, ClassLoader)
*/
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
实现类
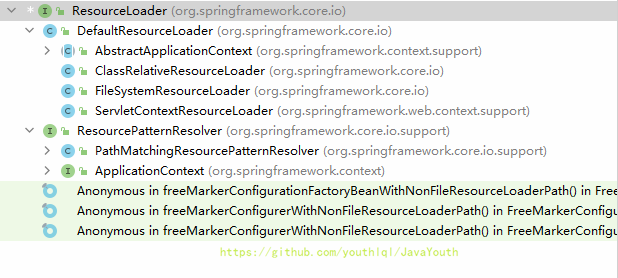
- DefaultResourceLoader:默认资源加载器
- ClassRelativeResourceLoader:能读取类路径相对路径
- FileSystemResourceLoader:能读取文件系统的
- ServletContextResourceLoader:能读取web环境的
BeanFactory-Bean工厂
/**
* The root interface for accessing a Spring bean container.
* 根接口,整个访问容器的入口
* <p>This is the basic client view of a bean container;
* further interfaces such as {@link ListableBeanFactory} and
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory}
* are available for specific purposes.
*
* <p>This interface is implemented by objects that hold a number of bean definitions,
* 保存很多的BeanDefinition信息,都有一个唯一的名字
* each uniquely identified by a String name. Depending on the bean definition,
* the factory will return either an independent instance of a contained object
* (the Prototype design pattern【原型模式】), or a single shared instance (a superior
* alternative to the Singleton design pattern【单例设计模式】, in which the instance is a
* singleton in the scope of the factory). Which type of instance will be returned
* depends on the bean factory configuration: the API is the same. Since Spring
* 2.0, further scopes are available depending on the concrete application
* context (e.g. "request" and "session" scopes in a web environment).
*
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
//省略...
}
源码分析小技巧:看源码时,我们可以先看一个类的接口继承关系,因为接口就是规范,大部分开源框架源码都是遵守这一规范的。
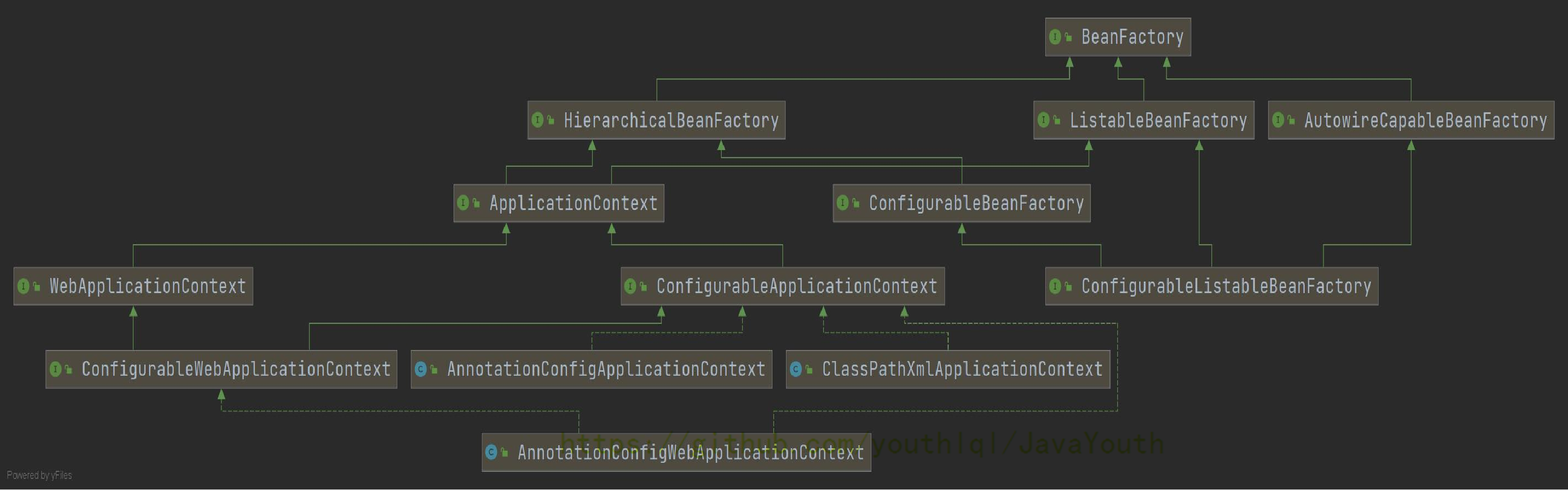
- BeanFactory
- HierarchicalBeanFactory:定义父子工厂(父子容器)
- ListableBeanFacotory:实现是DefaultListableBeanFactory,保存了ioc容器中的核心信息。
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory:提供自动装配能力
- AnnotationApplicationContext:组合了一个总的注册中心(DefaultListableBeanFactory),它有自动装配能力。
AbstractApplicationContext
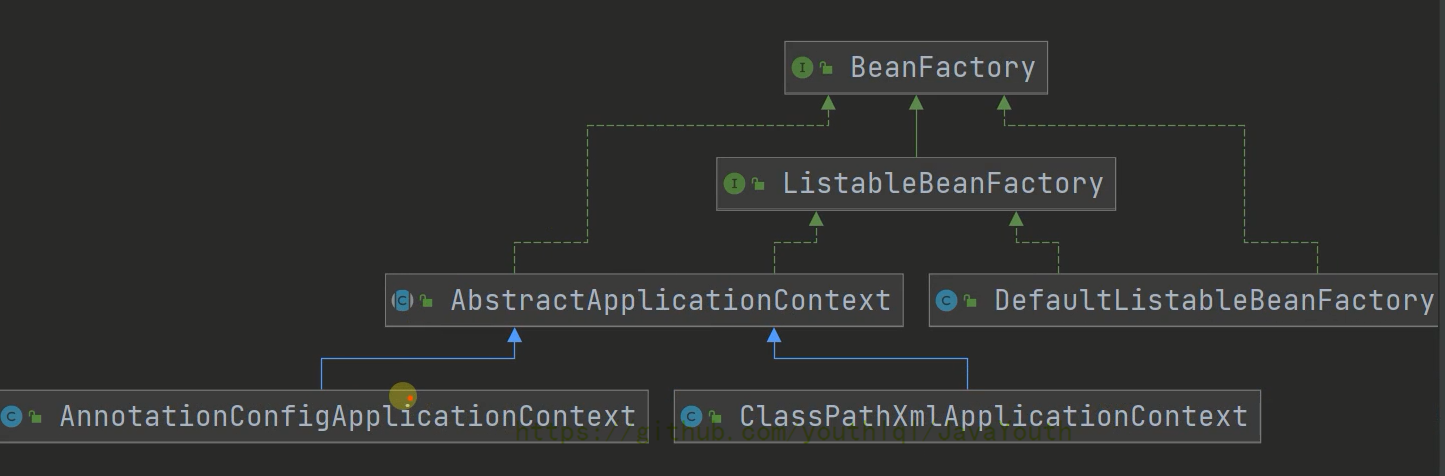
环境类的意思就是谁持有这个策略;这里就解释了上文说ResourceLoader是环境类接口
// 策略模式的环境类
private ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver;
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
GenericApplicationContext
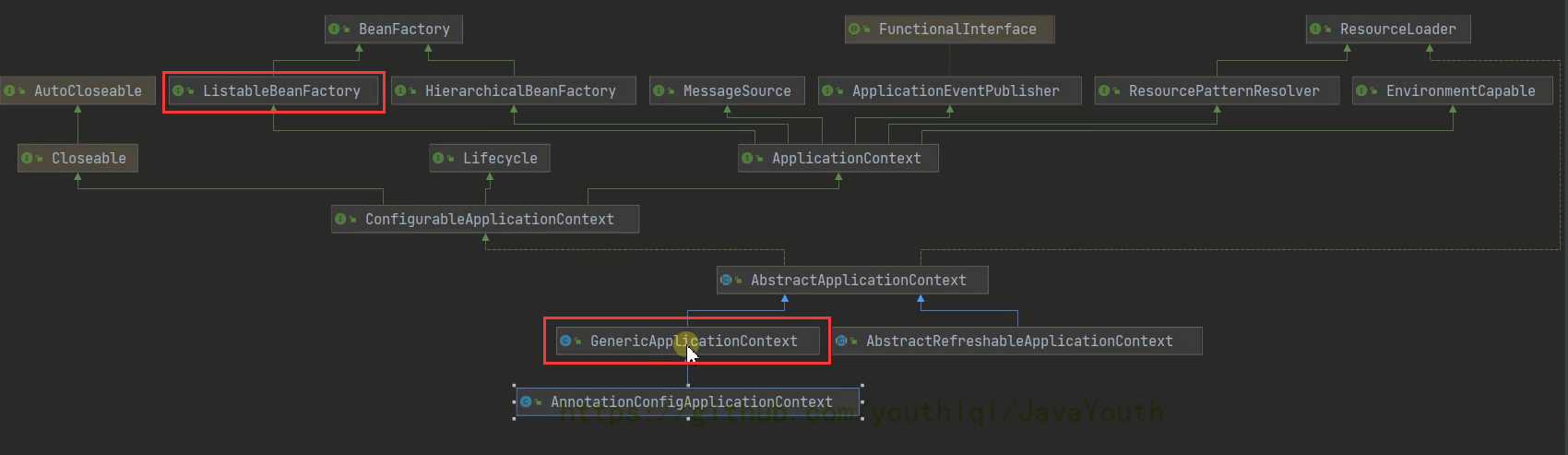
这里组合了DefaultListableBeanFactory
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
/** Map from serialized id to factory instance. */
//组合模式,Spring里面可以有很多工厂,每一个工厂有自己的ID,好处就是工厂之间的bean可以隔离起来,但是用的很少
private static final Map<String, Reference<DefaultListableBeanFactory>> serializableFactories =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>(8);
/**如果容器中有Map<Class, Object[]/String[] ></> Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name. */
//所有BeanDefinition信息按照名字对应BeanDefinition关系都保存好了。
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** Map of singleton-only bean names, keyed by dependency type. */
//Spring中按照类型得到组件的一个底层池
//车的图纸和车的关系。这里只保存图纸(也就是类信息),对象存哪里呢?往后看
private final Map<Class<?>, String[]> singletonBeanNamesByType = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
/** List of bean definition names, in registration order. */
//保存所有BeanDefinition的名字。
private volatile List<String> beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList<>(256);
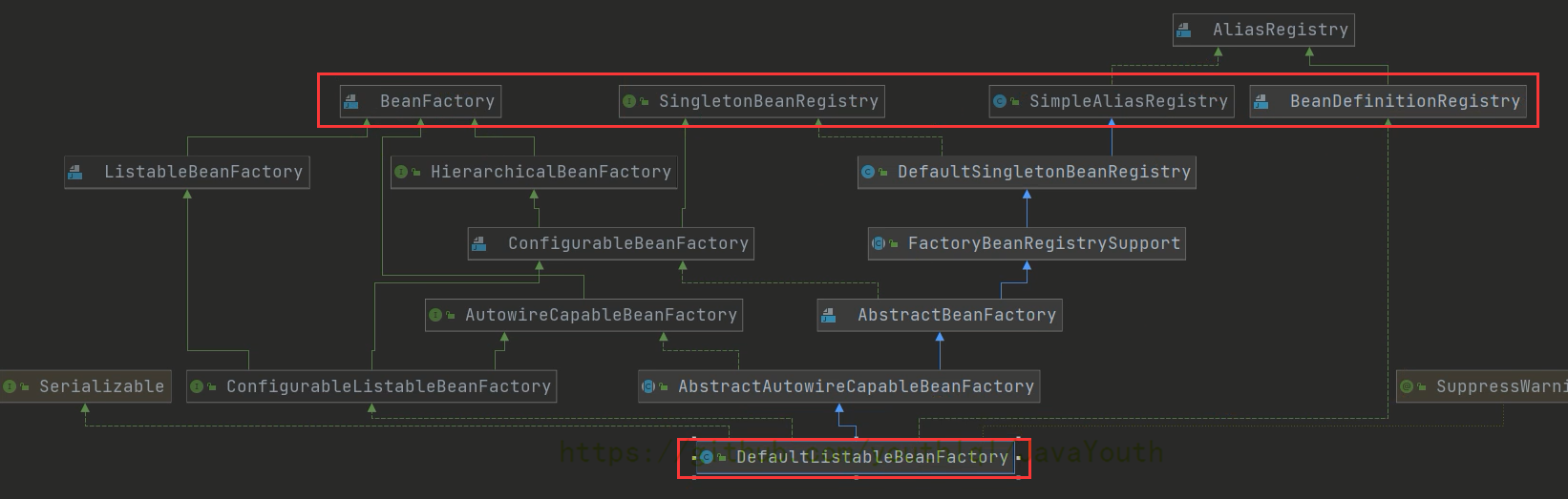
- BeanDefinitionRegistry:Bean定义信息注册中心
- SimpleAliasRegistry:别名注册中心
- SingletonBeanRegistry:单实例注册中心
- BeanFactory:Bean工厂
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory:有自动装配能力的Bean工厂
- DefaultListableBeanFactory:可以理解为拥有上面所有注册中心功能的一个总的注册中心
- GenericApplicationContext有一个我们常用的实现类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,就是注解版的IOC容器
- 虽然我们的IOC容器和DefaultListableBeanFactory没有继承的父子关系,但是却组合了DefaultListableBeanFactory,拥有了它的全部功能。
- DefaultListableBeanFactory在Spring中扮演着至关重要的角色。
- DefaultListableBeanFactory保存了所有对象(bean)的图纸(也就是类模板),并没有真正存对象。
- 我们这里猜想一下,Spring底层真正存Bean的地方用的是哪个数据结构呢?是List,还是Set,还是Map。咱们稍微想一下就知道肯定是Map,并且Key是beanName,value是真正的Bean。如果不是Map的话,如何通过BeanName拿到对应的Bean呢?
- 其实就是上面的那个beanDefinitionMap
注册BeanDefinition-1
流程图-BeanDefinition注册流程

- 我们要看BeanDefinition是何时被放入到beanDefinitionMap,只需要在DefaultListableBeanFactory用到
beanDefinitionMap.put()的地方打个断点。 - 我们在DefaultListableBeanFactory里搜索,发现了registerBeanDefinition(注册Bean定义信息)这个方法名很像我们要找的东西,再看里面的代码,果然有
beanDefinitionMap.put()这串代码,我们试着在这里打个断点 - 然后启动下面的测试类
- 上面就是我们看一个框架源码,可以往哪些方向去猜测。
MainTest测试类
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Person bean = context.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
Debug调用栈
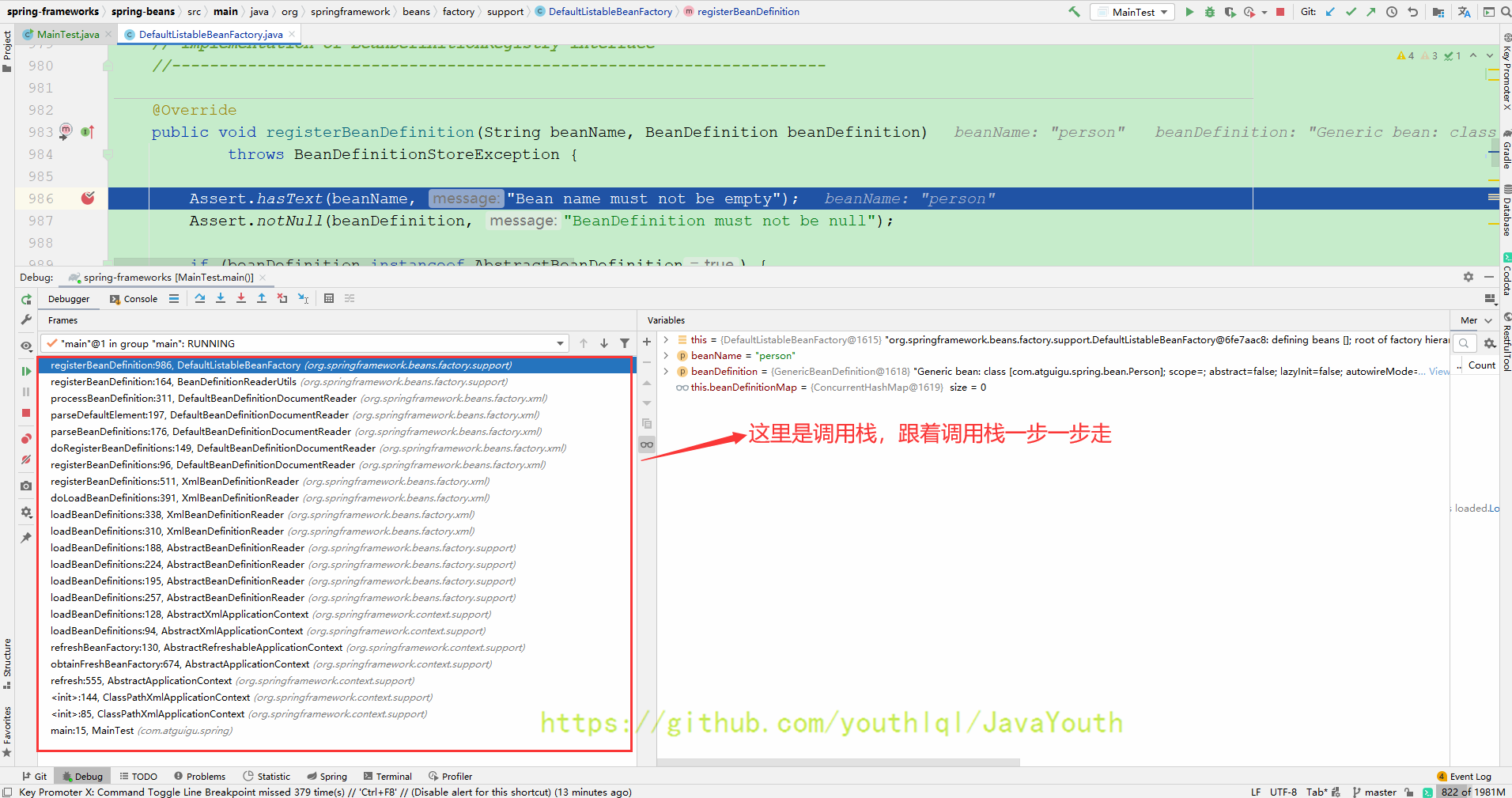
调用栈的调用顺序已经非常清楚了,可以把图放大一点看,下面只说一些必要的信息。
-
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml")这一步开始就要刷新容器了 -
调用
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()这个方法,refresh()方法是容器刷新的几大步所在地
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()容器刷新
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// BeanFactory第一次开始创建的时候,有xml解析逻辑。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// ......
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//完成 BeanFactory 初始化
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
// ......
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory()第一次开始创建BeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory(); //刷新整个BeanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()刷新整个BeanFactory
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); //创建保存所有Bean定义信息的档案馆
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); //开始加载Bean定义信息
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions()加载Bean定义信息
下面就是一堆的loadBeanDefinitions调用,调用顺序就是我下面写的代码顺序。
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. 准备读取xml内容的读取器
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); //持有ioc容器的环境类
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); //可以一次传入很多配置文件
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); //读取文件
}
}
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions()
下面也是一堆的loadBeanDefinitions调用,调用顺序就是我下面写的代码顺序。
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (String location : locations) { //加载每一个配置文件里面的内容
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return count;
}
@Override //加载指定配置文件的所有内容
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); //得到实体文件对应的资源
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL. 这里开始转换成我们前面说的Resource资源
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return count;
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions()
又是一堆loadBeanDefinitions调用
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 这里是个适配器模式 对接 InputStreamSource 和 Resource 或者说是个装饰器模式也可以
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); //利用dom解析工具把xml变成Document
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); //开始注册了
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions()注册Bean定义信息
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; //由这个类进行最终解析
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
//省略不重要的代码......
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
//省略不重要的代码......
//最后经过一些列的document文档遍历解析,走到了下面这个方法
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); //把当前标签解析完了,BeanDefinition和beanName都封装在了Holder中
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event. //发送一个通知事件
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils#registerBeanDefinition()
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any. 别名
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition()
//终于走到了这最后一步
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
//先看beanDefinitionMap有没有,没有我才注册
if (existingDefinition != null) {
//省略一系列目前来说不重要的判断......
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); //注册进去了
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
注册BeanDefinition-2
Debug调用栈
- 还有一个debug的猜测方向,想要注册BeanDefinition肯定要new,我们可以直接在AbstractBeanDefinition这个抽象父类的构造函数打断点,我们不知道会走哪个构造函数,所以给三个构造函数都打断点。
- 下面就是打完断点之后,运行MainTest测试类后的调用栈
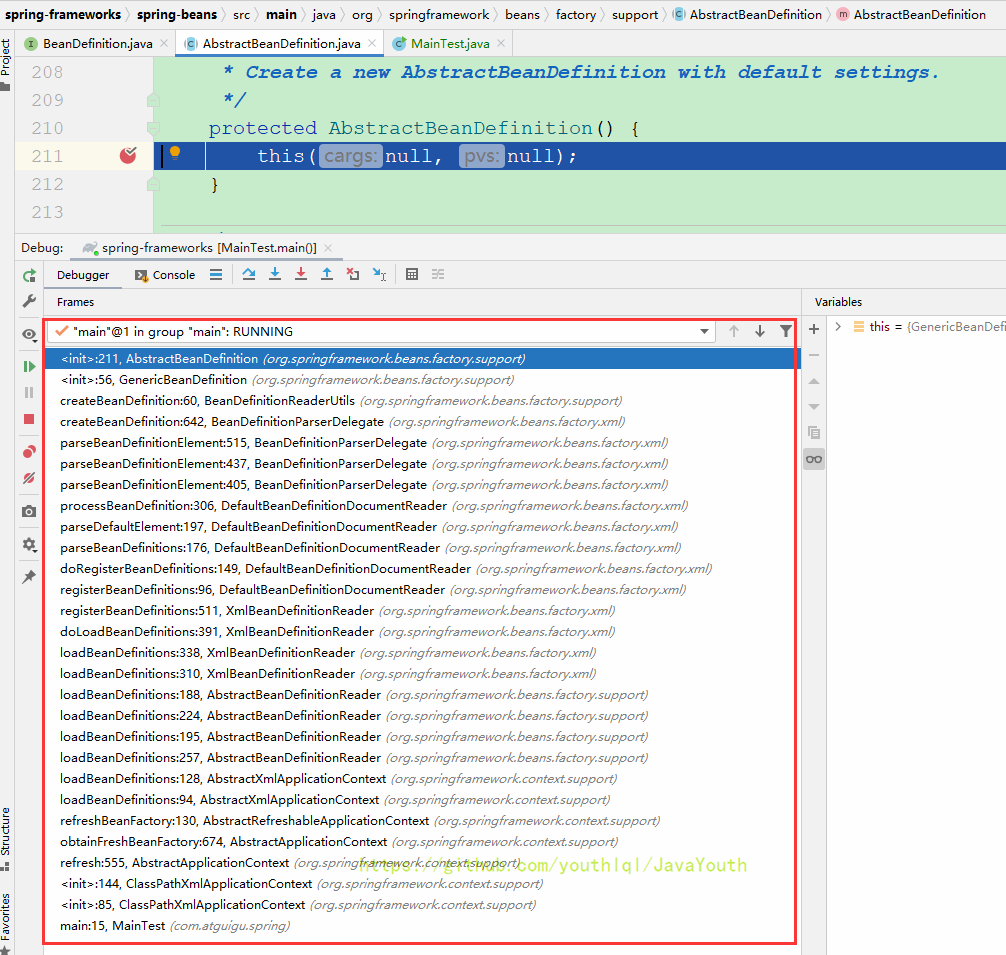
前面的调用栈都是一样的,从下面开始不一样
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#processBeanDefinition()
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); //把当前标签解析完了,BeanDefinition和beanName都封装在了Holder中
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event. //发送一个通知事件
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseBeanDefinitionElement()
public static final String ID_ATTRIBUTE = "id";
public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id; //为什么说id就是BeanName,Spring源码这里自己写的
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
// 省略部分代码......
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//以下是解析Bean标签里面的元数据填充完 BeanDefinition
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex); //这个就是我们常见的错误
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
protected AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(@Nullable String className, @Nullable String parentName)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition(
parentName, className, this.readerContext.getBeanClassLoader());
}
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils#createBeanDefinition()
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition(); //创建了一个BeanDefintion准备封装标签的内容
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
至此结束,上面的都不是很难,顺着调用栈就能看懂。
ApplicationContext接口功能
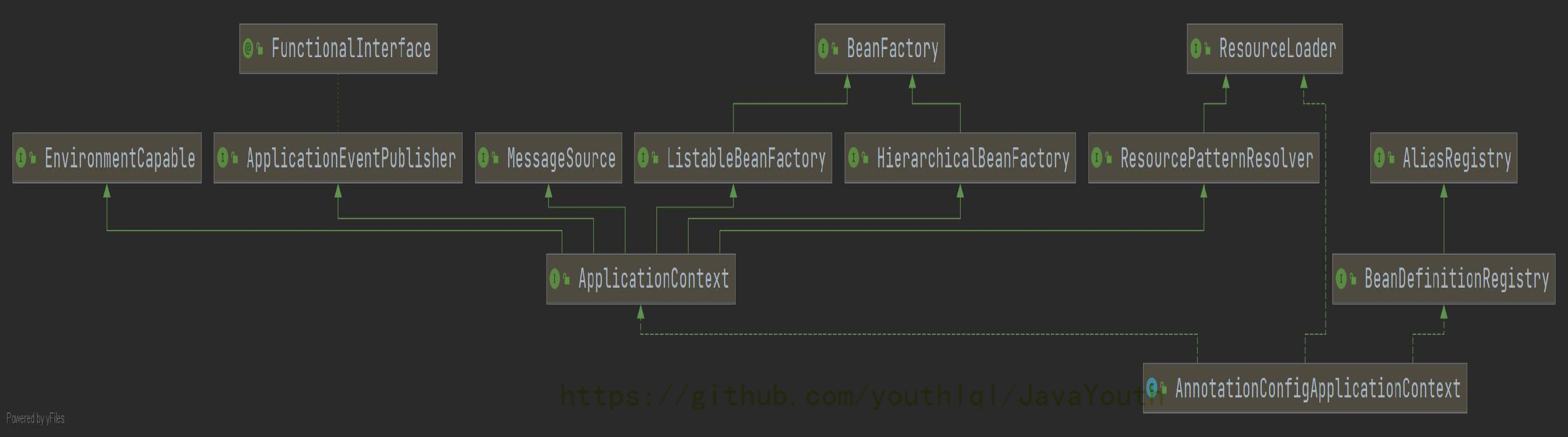
- ioc事件派发器
- 国际化解析
- bean工厂功能—自动装配被组合进来的
- 资源解析功能
- 等等
这个就是我们常说的IOC容器
Aware接口功能分析
- aware中文翻译是意识到的,察觉到的,发现这么个意思。从翻译来看,aware做的事情应该是发现某一个东西。
/**
* Marker superinterface indicating that a bean is eligible to be
* notified by the Spring container of a particular framework object
* through a callback-style method. Actual method signature is
* determined by individual subinterfaces, but should typically
* consist of just one void-returning method that accepts a single
* argument.
*/
public interface Aware {
}
- 注释的大致意思是:Aware是一个标记性的超接口(顶级接口),指示了一个Bean有资格通过回调方法的形式获取Spring容器底层组件。实际回调方法被定义在每一个子接口中,而且通常一个子接口只包含一个接口一个参数并且返回值为void的方法。
- 说白了:只要实现了Aware子接口的Bean都能获取到一个Spring底层组件。
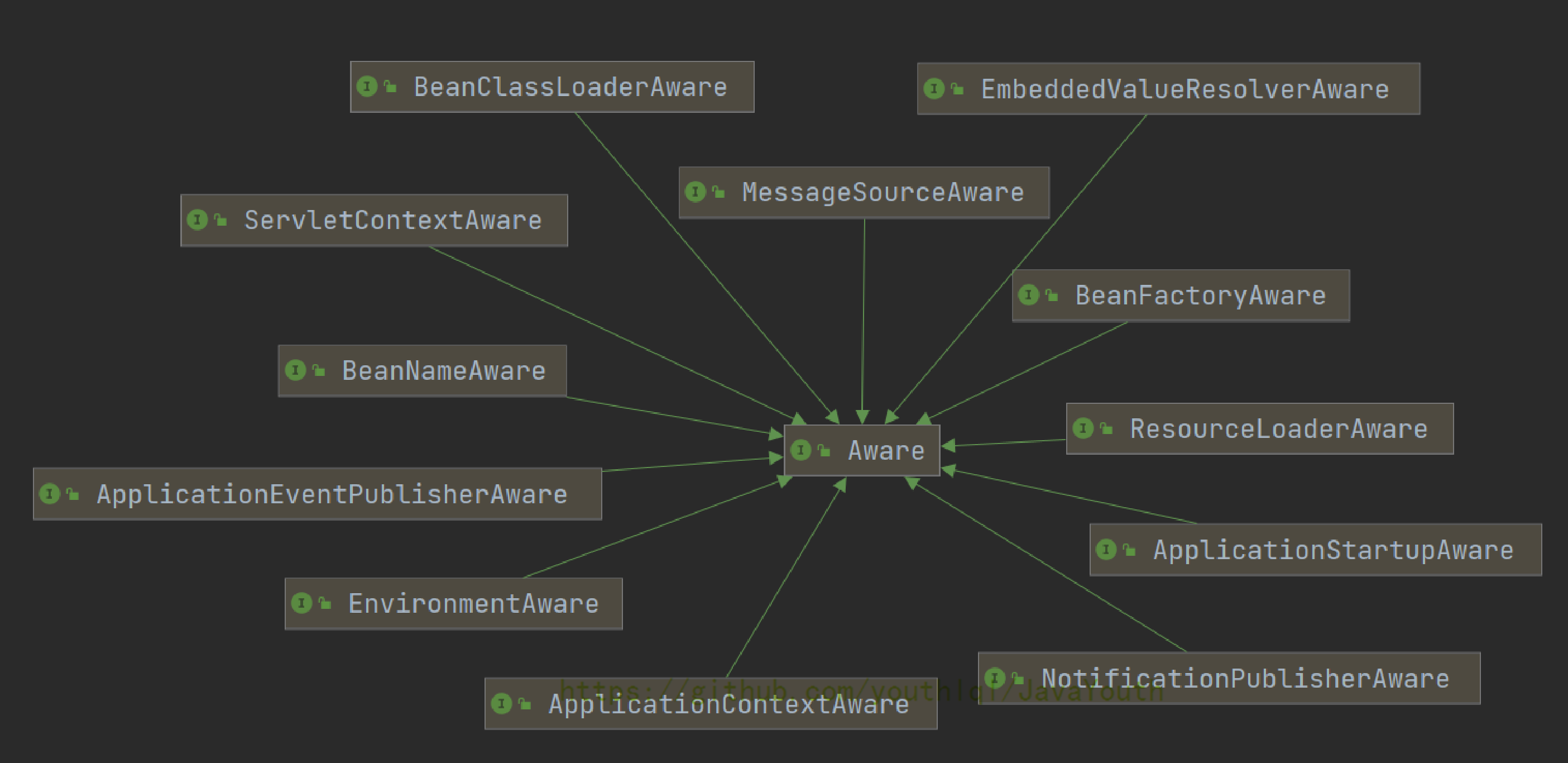
比如实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,实现它的方法,就能通过回调机制拿到ApplicationContext
创建Person对象
流程图-Bean对象创建流程
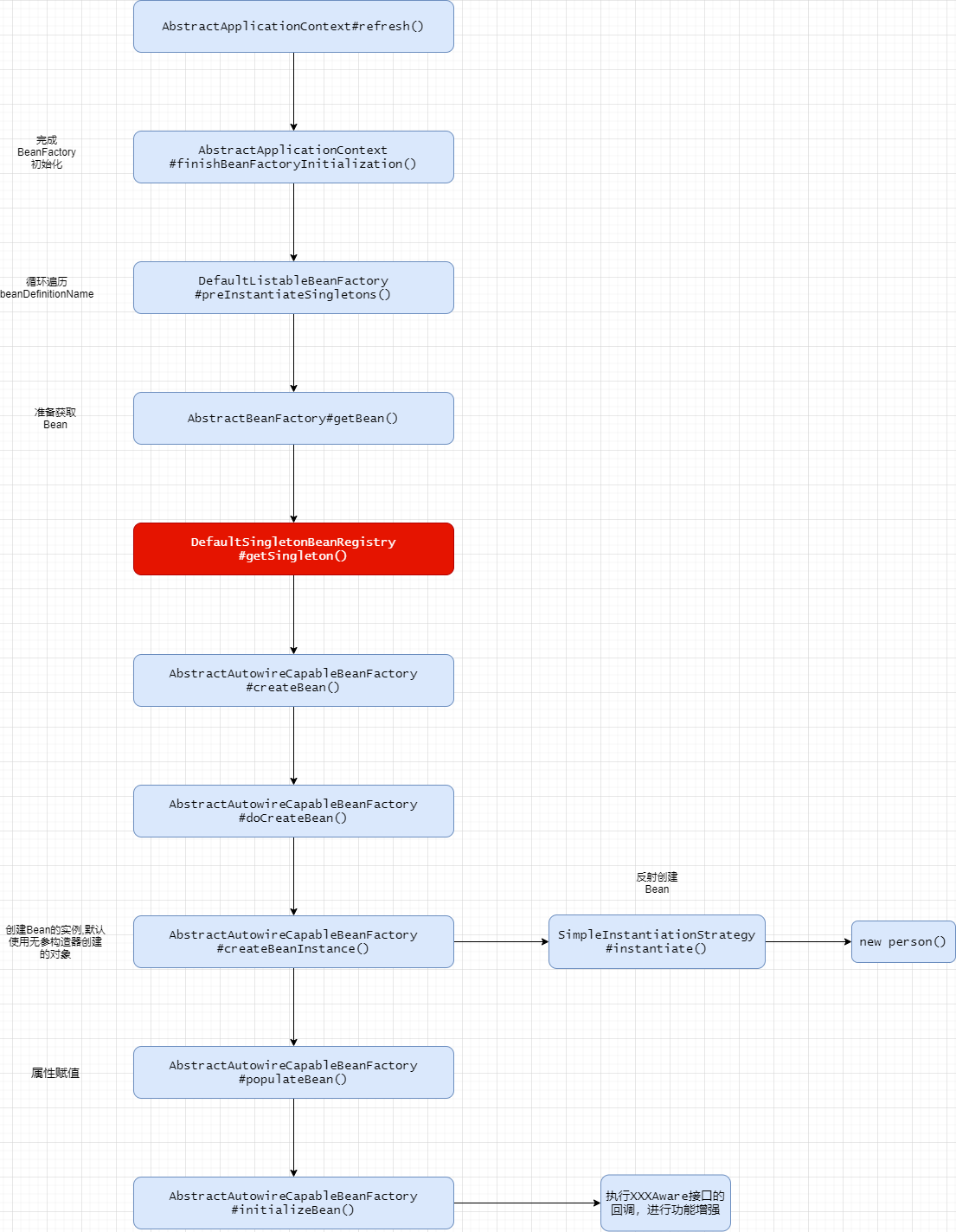
Debug调用栈
为了知道Aware的原理,我们给上面的pos_1和pos_2位置打上断点,看下是怎么进来的
Person
@Component
public class Person implements ApplicationContextAware, MessageSourceAware {
ApplicationContext context; //我们不用@Autowired也可以要到ioc容器
MessageSource messageSource;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Person(){
System.out.println("person创建...."); //pos_1
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
//利用回调机制,把ioc容器传入
this.context = applicationContext; //pos_2
}
@Override
public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
}
AnnotationMainTest
/**
* 注解版Spring的用法
*/
public class AnnotationMainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person bean = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
ApplicationContext context = bean.getContext();
System.out.println(context == applicationContext);
}
MainConfig
@ComponentScan("cn.imlql.spring")
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
public Person person(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("李四");
return person;
}
}
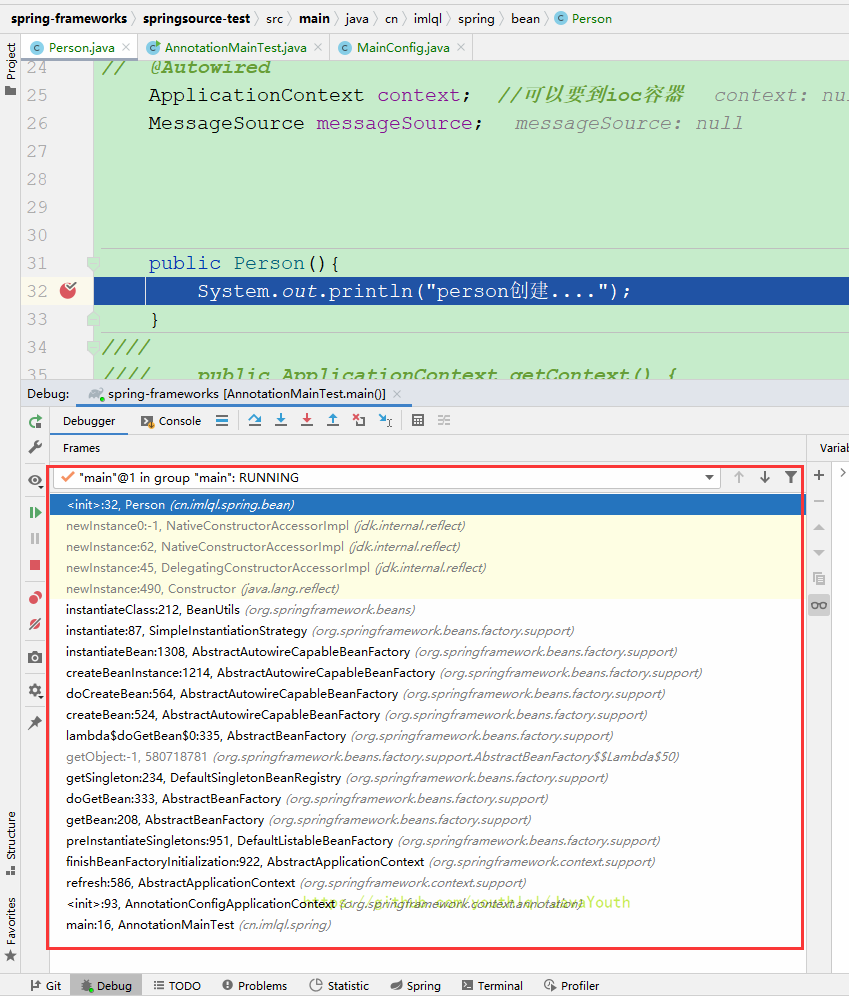
- 有一些一样的东西不再赘述
- 在
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()里会调用
AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()完成 BeanFactory 初始化
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// BeanFactory第一次开始创建的时候,有xml解析逻辑。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// ...
try {
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//完成 BeanFactory 初始化
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
}
}
}
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化所有的单实例Bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()循环遍历beanDefinitionName
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {//挨个遍历beanDefinitionName
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// ...
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
}
AbstractBeanFactory#getBean()准备获取Bean
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); //转换Bean名字
Object beanInstance;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); //检查缓存中有没有
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
//...
}
else {
//...
try {
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) { //看当前Bean有没有依赖其他Bean
try {
getBean(dep); //依赖了其他bean,就先获取其他的哪些bean
}
//...
}
}
// Create bean instance. 创建bean的实例,下面是一个lamda表达式
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); //创建bean对象的实例
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton()
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// ...
try {
// 通过getObject获取真正的对象,有点类似于FactoryBean(这个不懂的建议先了解下Spring基本用法),
// ObjectFactory类注释有说明。
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
// ...
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
下面就开始分析lamda表达式里的东西
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
//...
try {
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
}
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
//...
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建Bean的实例,默认使用无参构造器创建的对象
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
//...
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
/** 指定Bean的创建策略;可以用jdk的反射,可以用cglib创建子类对象 Strategy for creating bean instances. */
private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy;
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
else {
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
}
SimpleInstantiationStrategy#instantiate()反射创建Bean
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
}
Spring内部的BeanUtils反射工具
这个类是Spring内部提供的反射工具类,平时项目你也可以用上,就不用自己写反射了
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
else {
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
}
// 后面就是反射创建Person
Aware回调原理
Debug调用栈
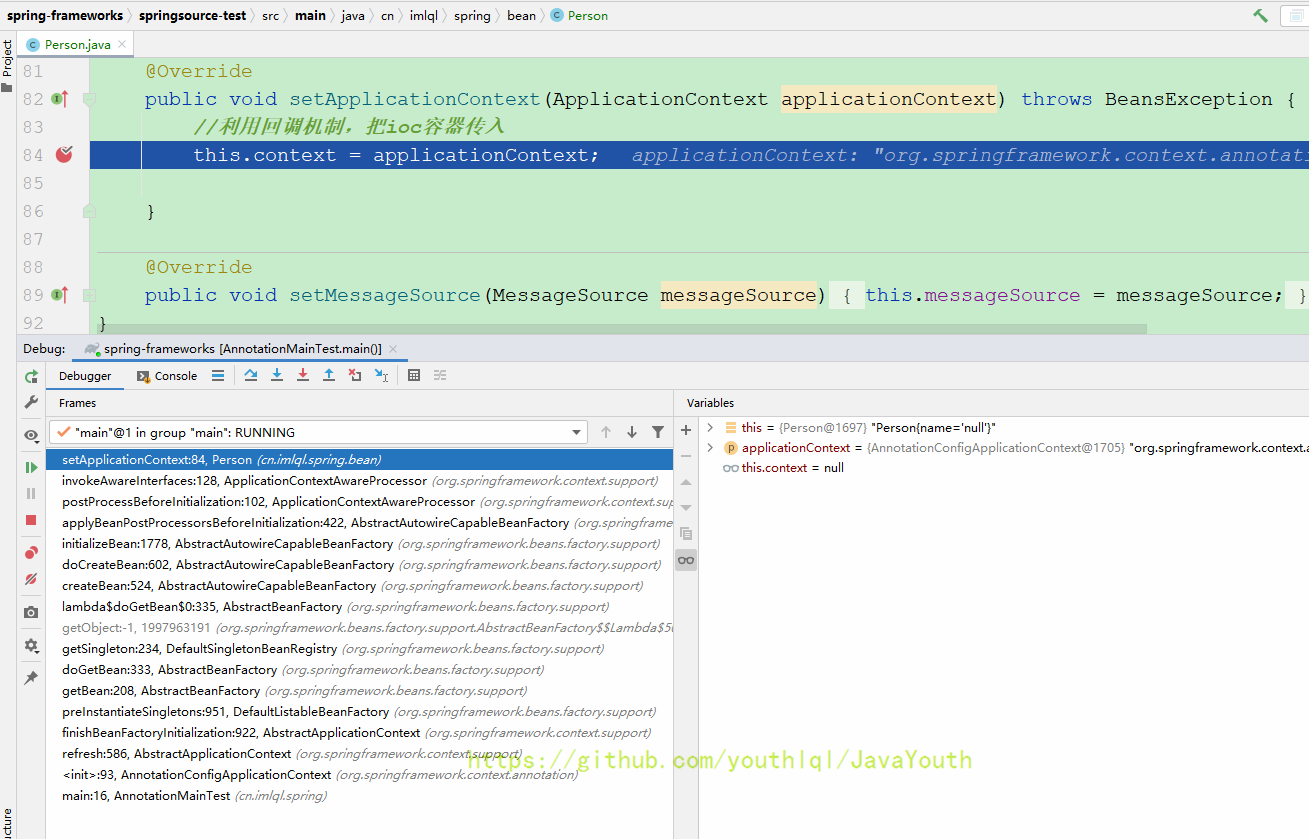
前面有很多一样的调用链,不再赘述。从doCreateBean:602调用栈开始不一样
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware ||
bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware)) {
return bean;
}
//...
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); //执行aware接口规定的方法
}
return bean;
}
//就是在这里执行Aware回调
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware) {
((ApplicationStartupAware) bean).setApplicationStartup(this.applicationContext.getApplicationStartup());
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
属性赋值的时机(XML版)
Debug调用栈
Person
public class Person implements ApplicationContextAware, MessageSourceAware {
ApplicationContext context; //我们不用@Autowired也可以要到ioc容器
MessageSource messageSource;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name; // pos_2
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Person(){
System.out.println("person创建...."); //pos_1
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
//利用回调机制,把ioc容器传入
this.context = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
}
MainTest
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Person bean = context.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean class="cn.imlql.spring.bean.Person" id="person">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
</bean>
</beans>
为了知道属性赋值的时机,这里要给setXXX方法打断点,也就是上面的pos_1和pos_2位置打断点。
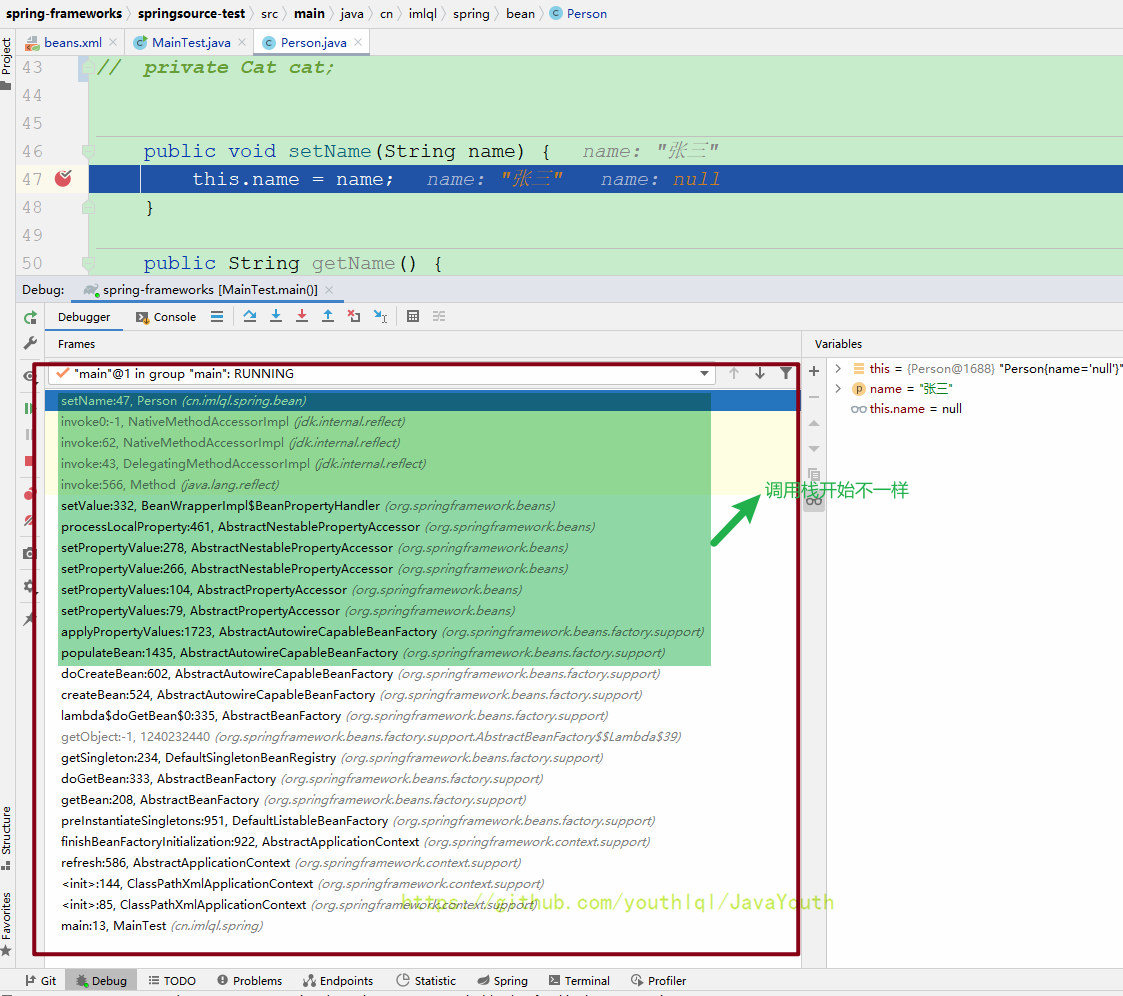
还是老规矩,一样的就不说了,从调用栈不一样的地方开始说起。多看几遍,看到后面就会发现思路越来越清晰了。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean. 这里面封装好了真正的Person对象
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建Bean的实例,默认使用无参构造器创建的对象
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//......
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //给创建好的对象每个属性进行赋值
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);//初始化bean
}
return exposedObject;
}
我们看到此时,Person的name属性还是null
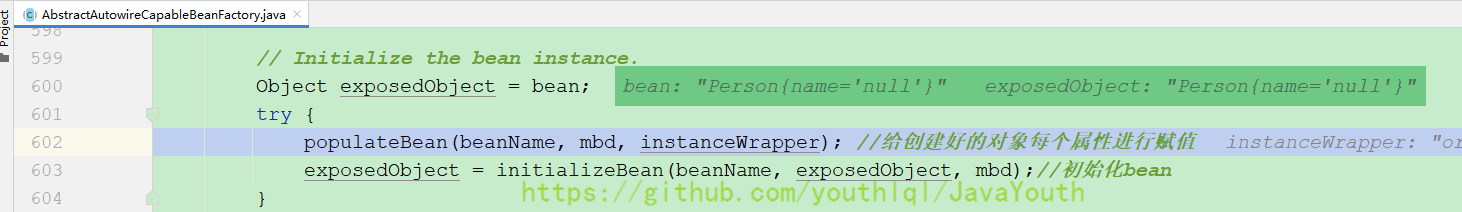
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean()属性赋值
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
// 这一步就是拿到属性值
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// ......
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); //xml版的所有配置会来到这里给属性赋值
}
}
这里拿到属性值
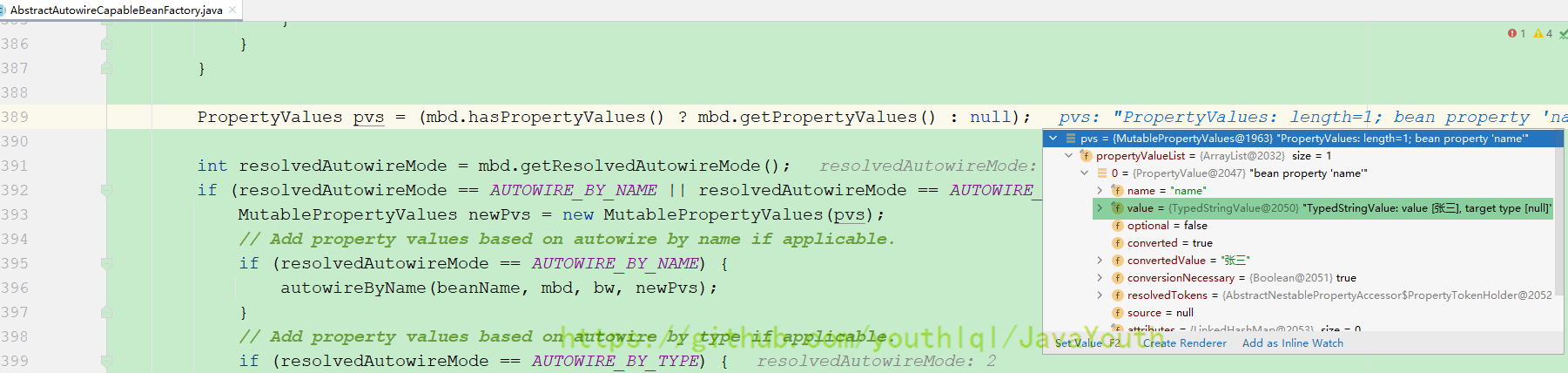
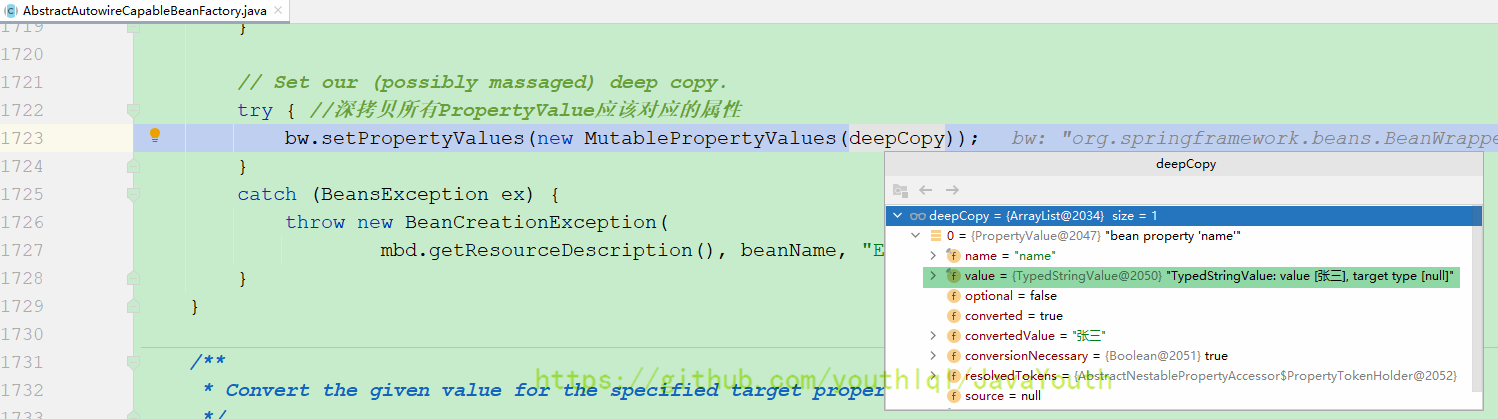
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
// ......
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try { //深拷贝所有PropertyValue应该对应的属性
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
}
bw就是上面说的 => 里面封装好了真正的Person对象
这里就是一层一层调,不重要跳过。

AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor#processLocalProperty
private void processLocalProperty(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) {
// ...
try {
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
Object valueToApply = originalValue;
ph.setValue(valueToApply);
}
//...
}
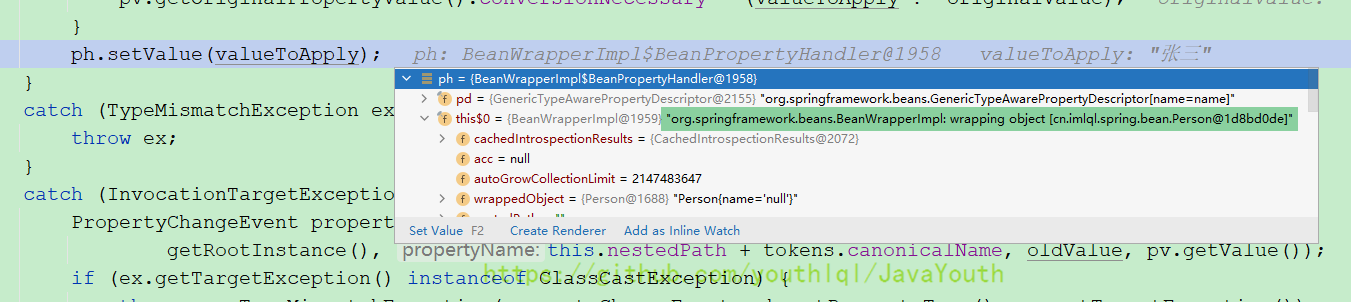
BeanWrapperImpl内部类BeanPropertyHandler#setValue()
private class BeanPropertyHandler extends PropertyHandler {
@Override
public void setValue(@Nullable Object value) throws Exception {
Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
// 这里的意思就是找到这个属性的写方法,所谓写方法就是setxxx方法
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}
}
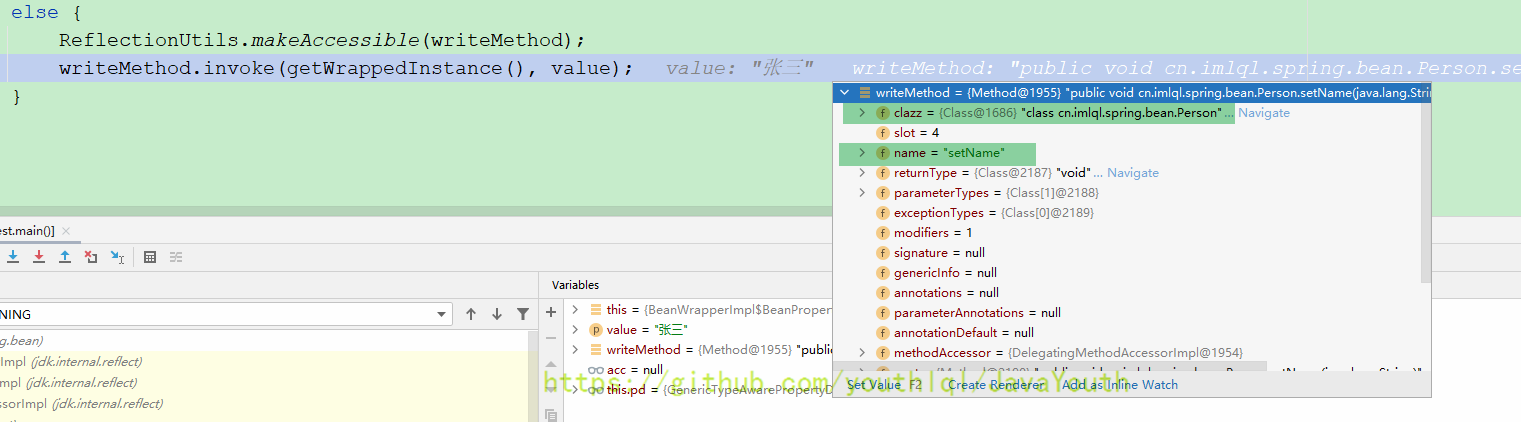
最后就是反射走到了我们的Person#setName(String name)
再来看看messageSource何时赋值
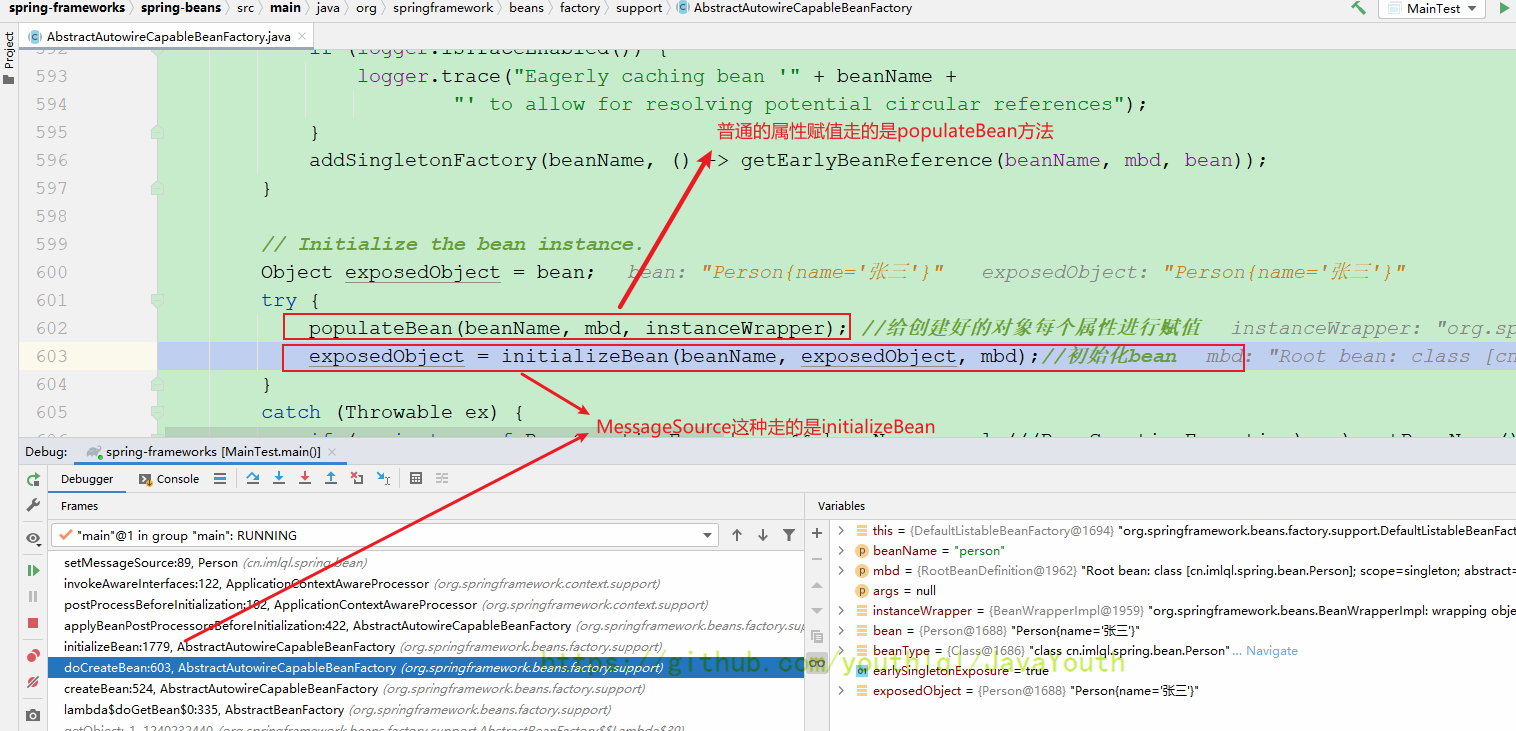
剩下的在上面的Aware回调原理讲过
属性赋值的时机(注解版)
Debug调用栈
AnnotationMainTest
public class AnnotationMainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person bean = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
ApplicationContext context = bean.getContext();
System.out.println(context == applicationContext);
}
}
Cat
@Component
public class Cat {
public Cat(){
System.out.println("cat被创建了...");
}
private String name;
@Value("${JAVA_HOME}") //自动赋值功能
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("cat....setName正在赋值调用....");
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
MainConfig
@ComponentScan("cn.imlql.spring")
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
public MainConfig(){
System.out.println("MainConfig...创建了....");
}
public Person person(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("李四");
return person;
}
}
Person
@Component
public class Person implements ApplicationContextAware, MessageSourceAware {
ApplicationContext context; //可以要到ioc容器
MessageSource messageSource;
private String name;
private Cat cat;
public Person(){
System.out.println("person创建....");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Autowired //去发现一下.....
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public ApplicationContext getContext() {
return context;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
//利用回调机制,把ioc容器传入
this.context = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
}
老样子,只看不一样的调用栈
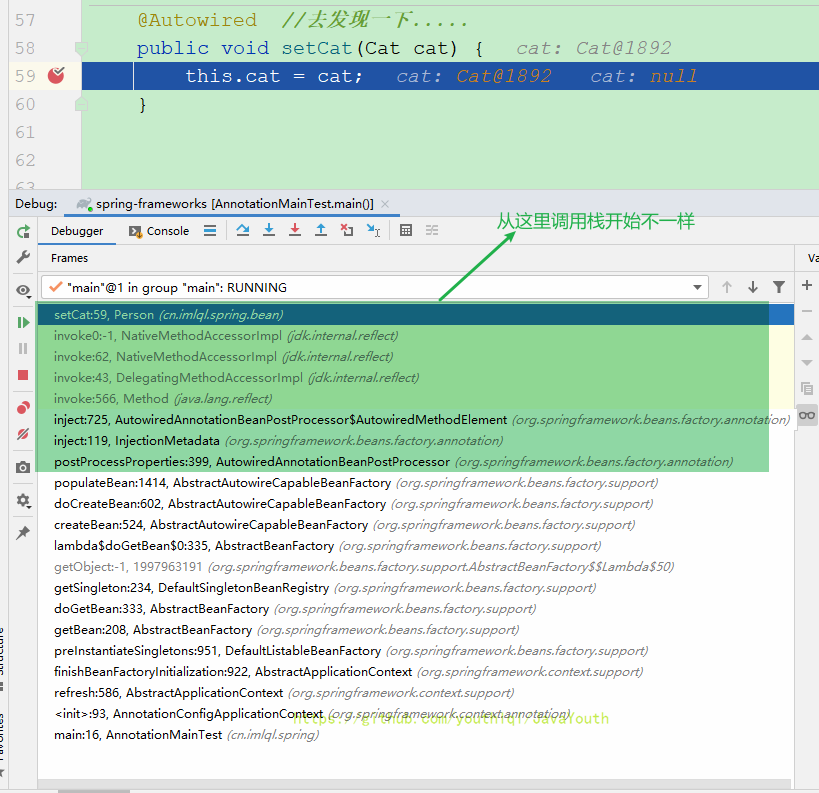
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean()
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
// ......
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
// 注解版的属性赋值会走这里
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = bp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); //xml版的所有配置会来到这里给属性赋值
}
}
这里有一个非常著名的后置处理器,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor自动装配注解后置处理器,顾名思义就是用来处理@Autowired注解自动装配的。
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties()
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);//找到自动装配的元信息
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
下面的代码不在debug调用栈里,但是也比较重要
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}//下面是分析当前类方法或者属性有没有标注@Autowired等自动赋值的注解
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//找所有属性中标注了@Autowired\@Value\@Inject注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//拿到所有方法,看有没有@Autowired注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
BeanUtils:Bean反射工具类
ReflectionUtils:真正操作反射的工具类
@Nullable
private MergedAnnotation<?> findAutowiredAnnotation(AccessibleObject ao) {
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(ao);
for (Class<? extends Annotation> type : this.autowiredAnnotationTypes) {
MergedAnnotation<?> annotation = annotations.get(type);
if (annotation.isPresent()) {
return annotation;
}
}
return null;
}
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> autowiredAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
InjectionMetadata#inject()
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor内部类AutowiredMethodElement#inject()
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
try {
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Unexpected removal of target bean for cached argument -> re-resolve
arguments = resolveMethodArguments(method, bean, beanName);
}
}
else {
arguments = resolveMethodArguments(method, bean, beanName);
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);// 这里就是反射调用setXXX了
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
BeanPostProcessor后置处理器贯穿整个Spring框架,Spring的事务,属性赋值,等等各方面都与其有着密不可分的关系,后面就开始讲BeanPostProcessor